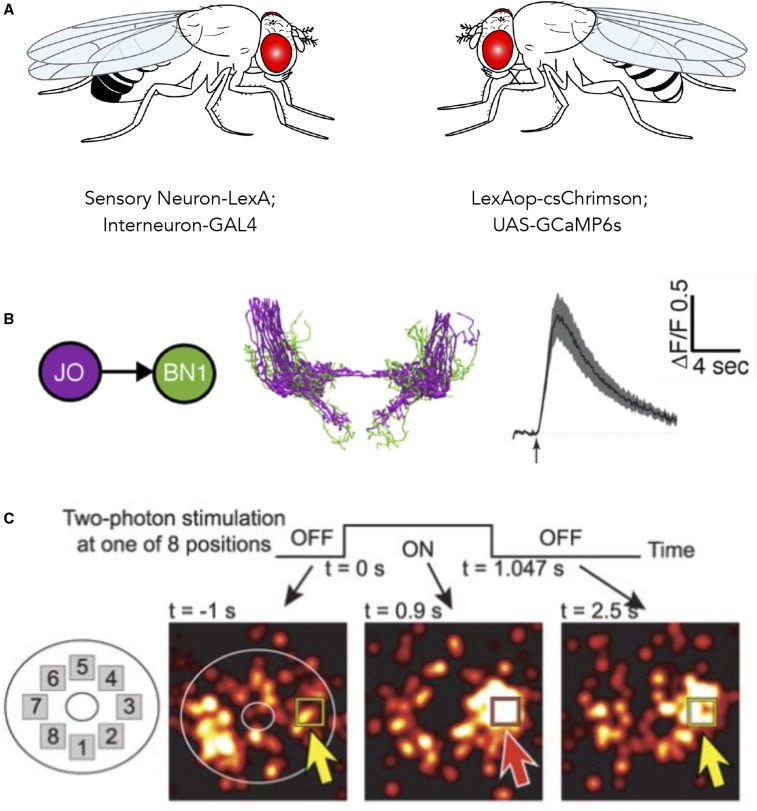
Figure 3.
Using optogenetics and functional imaging together. (A) Example cross scheme for functional connectivity mapping, showing independent transcriptional control of optogenetic activator and genetically encoded calcium reporter. (B) Excitation of CsChrimson (590 nm light-emitting diode through objective) in Johnston's Organ (JO) sensory neurons evokes changes in GCaMP6 fluorescence (Bruker two-photon 920 nm) in candidate postsynaptic interneurons Brain Neurons (BN1) in the antennal grooming circuit (Hampel et al. 2015). (C) Optogenetic activation of specific ellipsoid body neurons coexpressing CsChrimson and GCaMP6f shifts the location of the bump of population activity, suggesting mutual suppression consistent with ring attractor models of circuits that maintain a unique representation of an animal’s heading [figure 2C in Kim et al. (2017)].