Fig. 6.
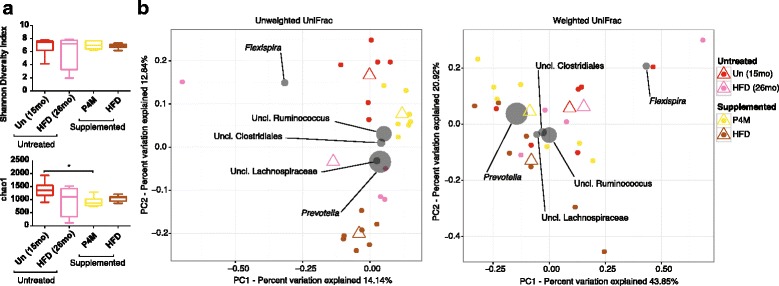
HFD challenge is associated with alterations in the gut microbiome. To reduce sampling heterogeneity, rarefaction was performed utilizing 3125 sequences from each sample. a Alpha diversity of synbiotic supplemented juveniles at 4-months post-supplementation and HFD challenge, and untreated juveniles at 15 months and during HFD challenge (26 months). 4-months post-supplementation juveniles were found to have a significant lower alpha diversity compared to untreated juveniles as measured by chao1 but not by Shannon. Statistical significance was tested using Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. Asterisk indicates a p ≤ 0.05. b PCoA displaying beta diversity (unweighted and weighted UniFrac) of synbiotic supplemented juveniles at 4-months post-supplementation, HFD challenge, and untreated juveniles at 15 months and during HFD challenge (26 months). Gray circles represent relative contributions in sample clustering for the top five genera. Open triangles represent centroids and ellipses indicate 95% confidence intervals. All groups were found to significantly cluster different from one another (unweighted UniFrac PERMANOVA, p = 0.001; weighted UniFrac PERMANOVA, p = 0.024). The juvenile cohort that received synbiotic supplementation was found to cluster separately from the cohort that did not receive synbiotic supplementation (unweighted UniFrac PERMANOVA, p = 0.001; weighted UniFrac PERMANOVA, p = 0.022). Abbreviations: Un (15mo): untreated juveniles at 15 months; HFD (26mo): untreated juveniles during HFD challenge at 26 months; P4M: treated juveniles at 4-months post-treatment; HFD: treated juveniles during HFD challenge
