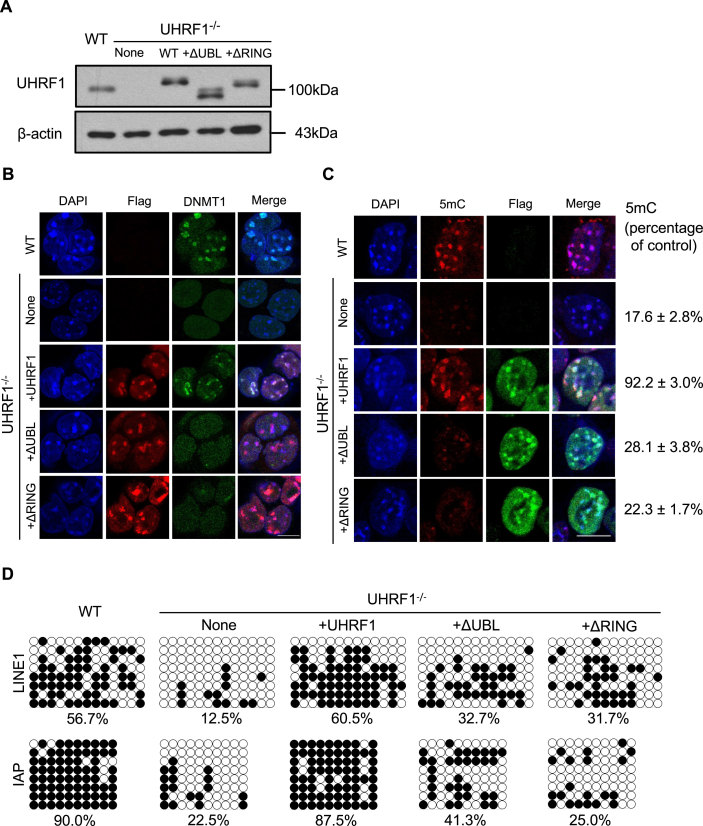
Figure 5.
Both UHRF1 UBL and RING finger are critical for DNMT1 proper nuclear localization and maintenance DNA methylation in mouse embryonic stem cells. (A) UHRF1−/− mouse ES cell lines stably expressing Flag-Myc-tagged UHRF1 wild-type or various mutants were analyzed by western blot using antibodies that recognize UHRF1. Flag-Myc-tagged UHRF1 or mutants expressed at a level similar to endogenous UHRF1 were selected for the study. β-actin was selected as a loading control. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of DNMT1 focal staining pattern in UHRF1 wild-type, UHRF1 knockout mouse ES cells and UHRF1−/− ES cells transfected with UHRF1-ΔUBL or UHRF1-ΔRING truncated mutant. Exogenous expression of UHRF1 and mutants was detected by Flag antibodies. Scale bars, 10 μm. (C) Immunostaining using an antibody against 5mC in control and UHRF1−/− mouse ES cells after genetic complementation with wild-type or UHRF1-ΔUBL or UHRF1-ΔRING. The 5mC levels relative to wild-type ESCs were shown. Error bars represent ± s.e.m. (D) The DNA methylation status of LINE1 and IAP was analyzed by bisulfite sequencing in wild-type ESCs (as control), UHRF1−/− ESCs and UHRF1−/- ESCs stably expressing UHRF1 wild-type, or UHRF1-ΔUBL or UHRF1-ΔRING mutants. The percentage of 5mC was calculated and shown.