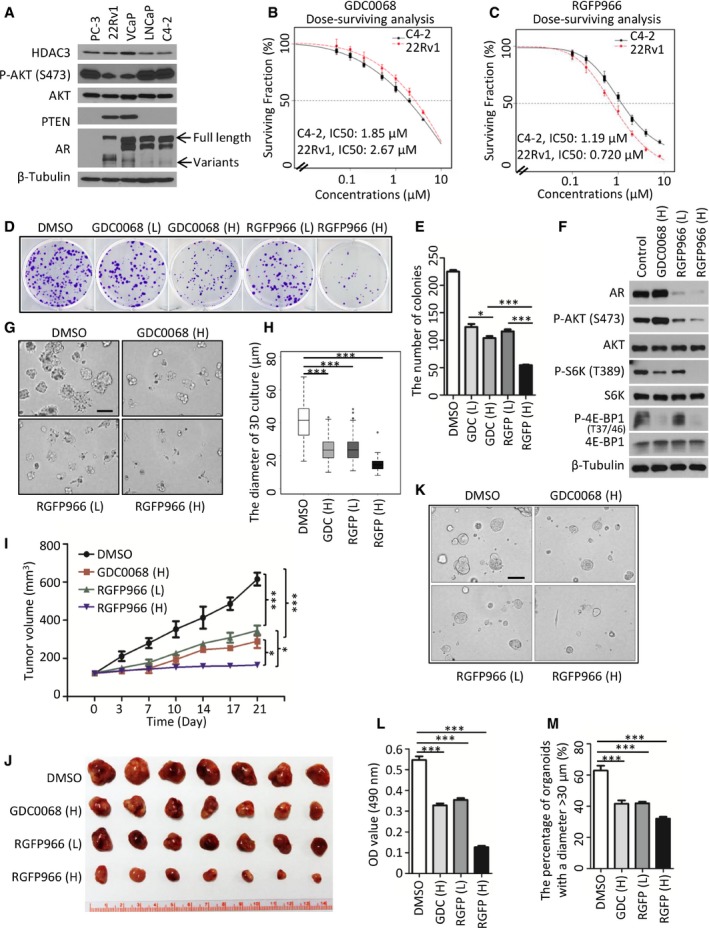
Figure 7. The HDAC3 inhibitor suppresses PTEN‐deficient prostate cancer growth.
-
ACell lysate was prepared from indicated prostate cancer cell lines for Western blot analysis. Arrows show the full length and variants of AR.
-
B, CC4‐2 and 22Rv1 cells were treated with GDC0068 (B) and RGFP966 (C). IC50 is shown as a dotted line in the middle of the graph; for C4‐2 cells, IC50 of GDC0068 = 1.85 μM; IC50 of RGFP966 = 1.19 μM; for 22Rv1 cells, IC50 of GDC0068 = 2.67 μM; IC50 of RGFP966 = 0.72 μM. The survival curve was generated from three independent experiments and each experiment was in triplicate. The error bars indicate the smallest and largest value among three independent experiments, which represented by lower whisker and upper whisker, respectively.
-
D, EC4‐2 cells were treated with low (L, 1× IC50) or high (H, 2× IC50) concentrations of GDC0068 or RGFP966 for 4 days. The number of colonies with more than 50 cells was counted. Representatives of colonies are shown in (D) with quantification data shown in (E). Data represent means ± SEM; GDC (L) versus GDC (H): *P = 0.037; GDC0068 (H) versus RGFP (H): ***P = 1.47e‐05, RGFP (L) versus RGFP (H): ***P = 3.55e‐05 were performed by the unpaired two‐tailed Student's t‐test.
-
FC4‐2 cells were treated with GDC0068 or RGFP966 for 24 h followed by Western blots.
-
G, HRepresentative images of 3D cultures of C4‐2 cells at day 5 post‐treatment of GDC0068 (H), RGF966 (L), or RGF966 (H) as shown in (G) with quantification data shown in a box plot (H). Each box in the graph indicates the interquartile range (IQR). The horizontal line represents the median value. Box lower limit is the first quantile (Q1) while the upper limit is the third quantile (Q3). The lower whisker is max(min(x)), Q1 – 1.5*IQR while the upper whisker is min(max(x)), Q3 + 1.5*IQR. DMSO (n = 144) versus GDC (H) (n = 180): ***P = 2.23e‐32, DMSO versus RGFP (L) (n = 233): ***P = 1.04e‐36 and DMSO versus RGFP (H) (n = 83): ***P = 3.12e‐35 were performed by Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction. Scale bar, 100 μm.
-
I, JMice with C4‐2 xenograft tumors were treated with vehicle (DMSO), GDC0068 (H) (50 mg/kg), RGFP966 (L) (25 mg/kg), or RGFP966 (H) (50 mg/kg) 5 days a week for three consecutive weeks (I). Images of tumors isolated at day 21 are shown in (J). Data are shown as means ± SEM. DMSO (n = 7) versus GDC0068 (H) (n = 7): ***P = 4.18e‐10, DMSO versus RGFP966 (L) (n = 7): ***P = 1.40e‐09, GDC0068 (H) versus RGFP966 (H) (n = 7): *P = 0.0182, RGFP966 (L) versus RGFP966 (H): *P = 0.0104 comparing the tumor volume at day 21 post‐treatment by the unpaired two‐tailed Student's t‐test.
-
K–MRepresentatives of organoids at day 5 post‐treatment of GDC0068 (H), RGF966 (L), or RGF966 (H) are shown in (K) with quantification data of OD value at 490 nm in (L). The OD value was measured and quantified from three biological replicates. Data represent means ± SEM; DMSO versus GDC0068 (H): ***P = 2.18e‐05; DMSO versus RGFP966 (L): ***P = 1.43e‐04, DMSO versus RGFP966 (H): ***P = 1.40e‐08 were performed using the unpaired two‐tailed Student's t‐test. Based on the observed growth rate of untreated PTEN‐deleted organoids, greater than 50% of organoids reach 30 μm in diameter at day 5. “30 μm” was set as the cutoff value. The number of organoids with the diameter > 30 μm from at least five fields (each field contains at least 7 organoids) were counted and analyzed from three biological replicates (M). Data are shown as means ± SEM; DMSO versus GDC0068 (H): ***P = 8.02e‐05; DMSO versus RGFP966 (L): ***P = 1.39e‐04, DMSO versus RGFP966 (H): ***P = 2.96e‐06 were performed by the unpaired two‐tailed Student's t‐test. Scale bar, 100 μm.
Source data are available online for this figure.
