Figure 4.
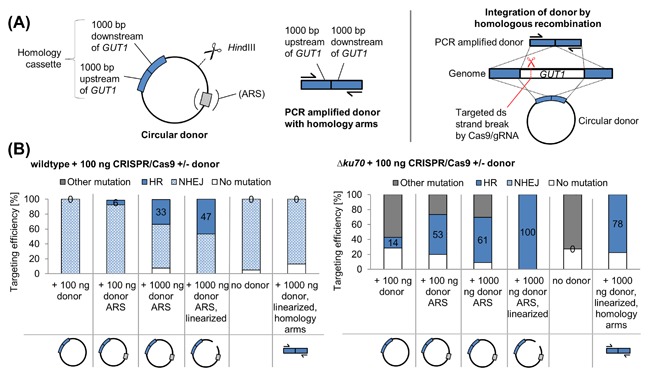
ARSs promote efficient CRISPR/Cas9 mediated integration of markerless donor fragments in the P. pastoris wildtype strain. A, Design of the donor cassettes (left side) and recombination events targeted (right side). A circular plasmid was used for the P. pastoris transformation, which contains 1000 bp regions 5′ upstream and 3′ downstream of GUT1 (and an ARS for replication in yeast). As control the PCR amplified homology cassette consisting of the 1000 bp regions 5′ upstream and 3′ downstream of GUT1 was used for the transformation. Due to sequence homology of the donor cassette the GUT1 CDS can be removed by homologous recombination. B, P. pastoris wildtype (left side) and Δku70 (right side) co‐transformation with 100 ng CRISPR‐Cas9 plasmid DNA (GUT1‐gRNA2) and various donor fragments: 100 ng circular donor DNA lacking ARS, 100 ng circular donor DNA with ARS, 1000 ng circular donor DNA with ARS, 1000 ng circular donor DNA with ARS linearized with HindIII, no donor DNA and 1000 ng PCR amplified donor DNA. Results on the PCR amplified donor cassette in the wildtype strain have previously been reported.32 Upon cultivating random transformants in 96‐DWPs, cell material was transferred with a metallic stamp on minimal media agar plates with either glucose (BMD1) or glycerol (BMG1) as carbon source to determine the targeting efficiency. The percentages of HR integrated donor fragments are denoted as numbers in the bar diagram. The integration of the donor cassettes was verified by sequencing of >10 glycerol deficient transformants per CRISPR/Cas9 plasmid—donor DNA combination. The ARS‐donor enables the integration of marker‐less donor fragments in almost 50% of the transformants, when 1000 μg linear donor DNA were used
