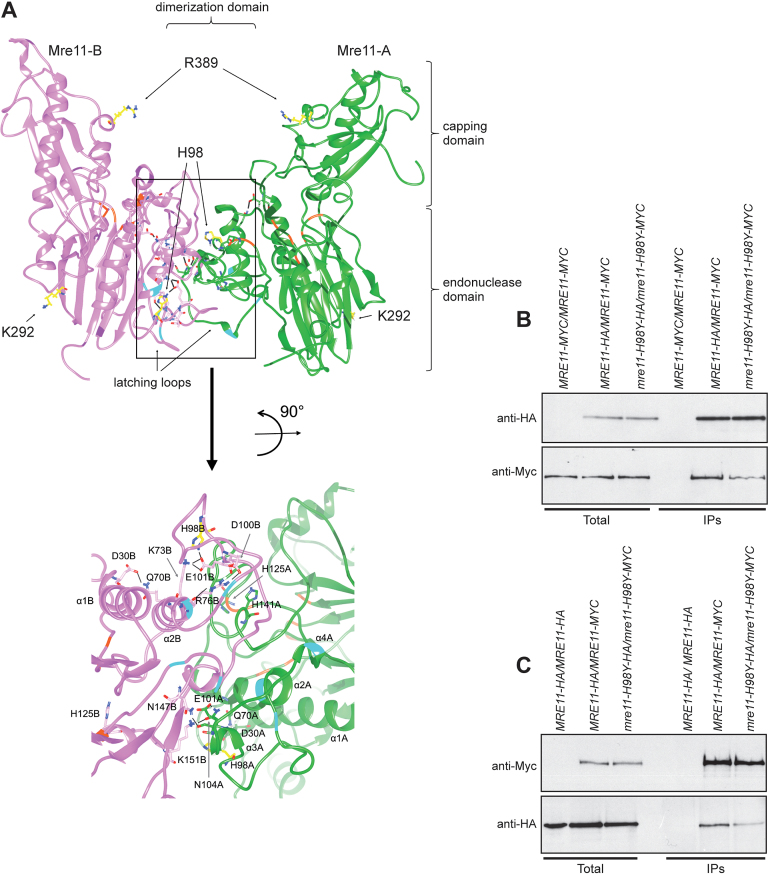
Figure 6.
Mre11-H98Y alters Mre11 dimer formation. (A) Structural prediction of S. cerevisiae Mre11 dimer, obtained by homology modelling and refined by molecular dynamics. The two Mre11 monomers are shown in green (Mre11-A) and pink (Mre11-B). The position of endonuclease, capping and dimerization domains are shown. The lateral chain is shown for the residues (in yellow) whose mutations were described in the text. A close-up view of the dimerization domain is shown at the bottom. On the ribbon, positions involved in direct interaction with Xrs2 are in cyan, while positions constituting the active site are in orange. Black bars represent the hydrogen bonds/salt bridges existing in this particular conformation. (B, C) Mre11 dimer formation. Protein extracts prepared from exponentially growing diploid cells with the indicated genotypes were analyzed by western blotting with anti-HA and anti-Myc antibodies either directly (Total) or after immunoprecipitation (IPs) with anti-HA antibody (B) or anti-Myc antibody (C).