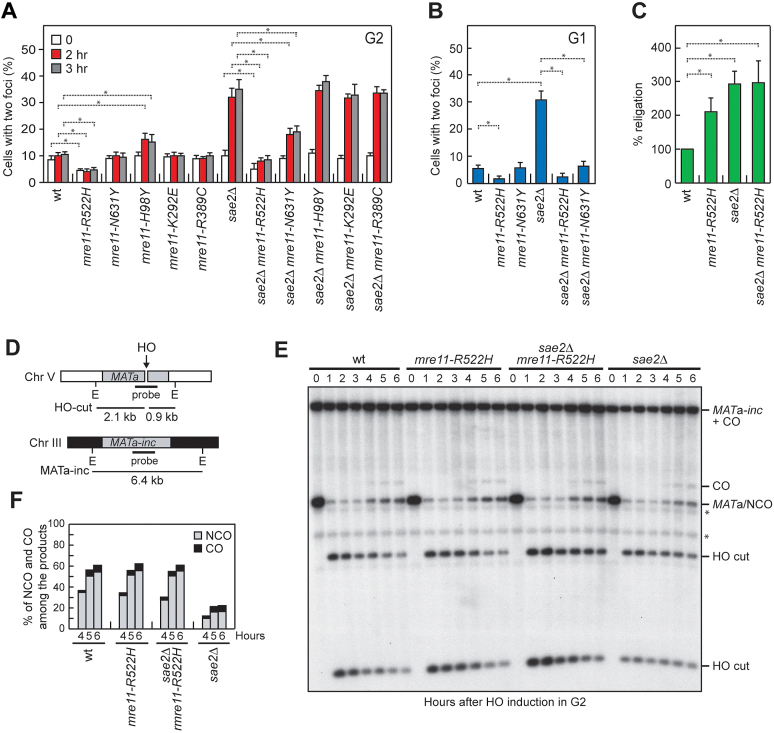
Figure 8.
Mre11-R522H suppresses the end-tethering and the HR defects of sae2Δ cells. (A, B) DSB end-tethering. Exponentially growing YEPR cell cultures were arrested in G2 with nocodazole (A) or in G1 with α-factor (B) at time zero and transferred to YEPRG in the presence of nocodazole or α-factor, respectively. 200 cells for each strain were analyzed to determine the percentage of cells showing two LacI-GFP foci. Plotted values are the mean values with error bars denoting S.D. (n = 3). *P< 0.05 (Student's t-test). (C) Plasmid re-ligation assay. Cells were transformed with BamH1-linearized or uncut pRS316 plasmid DNA. Data are expressed as percentage of re-ligation relative to wild type that was set up at 100% after normalization to the corresponding transformation efficiency with the uncut plasmid. Plotted values are the mean values with error bars denoting S.D. (n = 3). *P< 0.05 (Student's t-test). (D) System to detect ectopic recombination. HO generates a DSB at a MATa DNA sequence inserted on chromosome V, while the homologous MATa-inc region on chromosome III cannot be cut by HO and is used as a donor for HR-mediated repair. E, EcoRI. (E) YEPR cell cultures arrested in G2 with nocodazole were transferred to YEPRG at time zero in the presence of nocodazole. Southern blot analysis of EcoRI-digested genomic DNA with the MATa probe depicted in D. * indicates cross hybridization signals. (F) Densitometric analysis of CO versus NCO repair bands at the indicated times after HO induction.