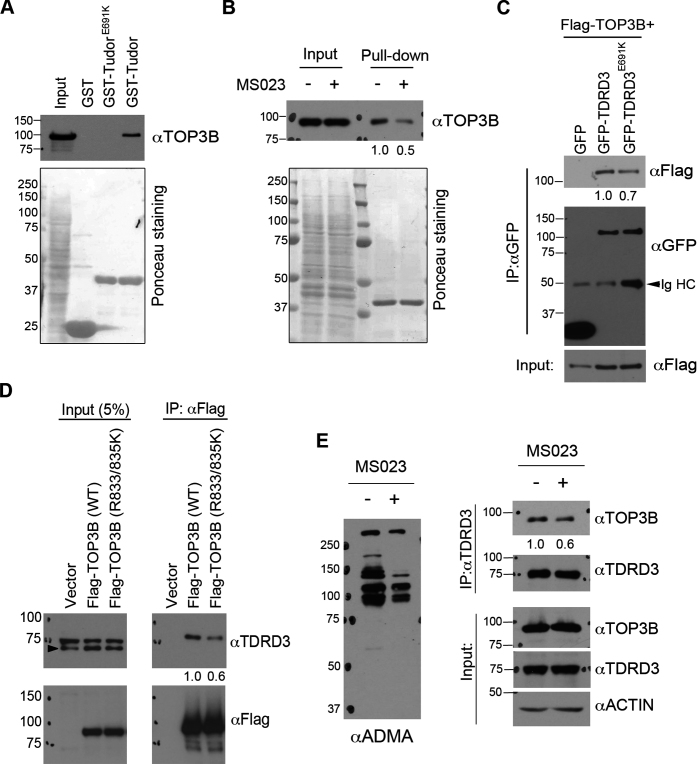
Figure 6.
The Tudor domain of TDRD3 interacts with TOP3B in a methylation-dependent manner. (A) GST-pulldown was performed by incubating recombinant wild-type and methylarginine-binding deficient (E691K) Tudor domain of TDRD3 with HeLa total cell lysate. The pulldown samples were detected using an anti-TOP3B antibody by western blots. The membrane was stained with Ponceau S to visualize the recombinant proteins used. (B) GST-pulldown was performed by incubating recombinant TDRD3 Tudor domain with HeLa cell lysate either untreated or pretreated with MS023 for 2 days. The samples were processed as described in (A). (C) Co-immunoprecipitation experiments were performed by transfecting HeLa cells with Flag-TOP3B and GFP-tagged variants of either wild-type or Tudor domain mutant (E691K) TDRD3. Anti-GFP antibody was used for immunoprecipitation. The samples were detected by western blots using antibodies as indicated. IgHC: IgG heavy chain. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation experiment was performed by transfecting HeLa cells with Flag-tagged variants of either wild-type or methylation-deficient (R833/835K) TOP3B. Anti-Flag antibody was used for immunoprecipitation. (E) Inhibition of arginine methylation reduces TOP3B and TDRD3 interaction. Co-immunoprecipitation experiment was performed in control and MS023-treated HeLa cells. Anti-TDRD3 antibody was used for immunoprecipitation. Quantification of the immunoblotting images was performed using ImageJ software. The relative ratio of IP signals for MS023 treated (B and E), Tudor mutant (E691K) (C) and methylation-deficient TOP3B (R833/835K) (D) were calculated using the signals of the wild-type or untreated protein as the standard (set as 1.0) and were listed below each image.