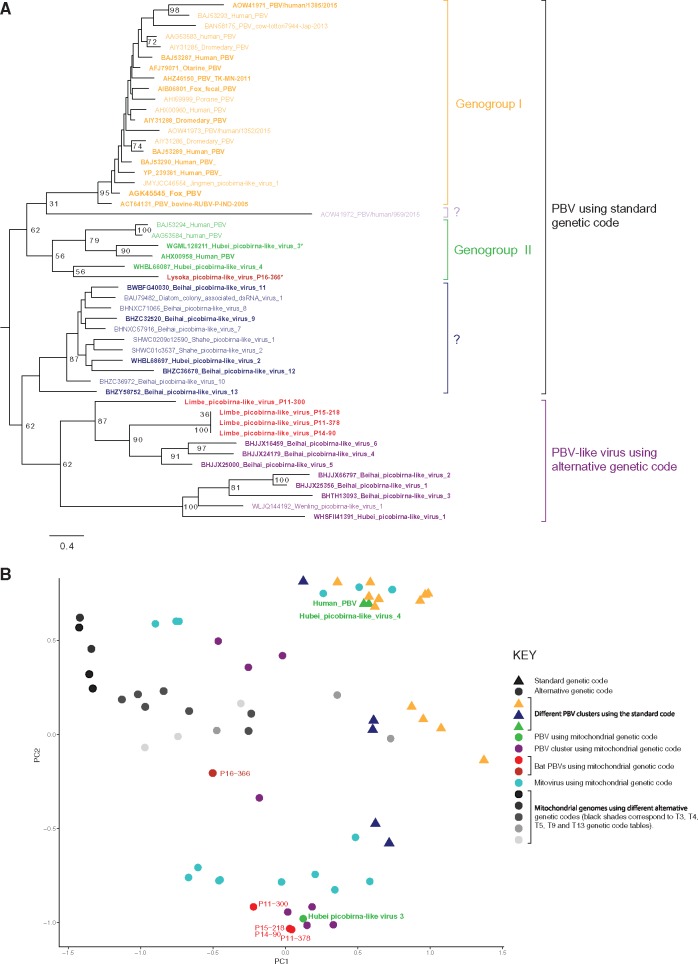
Figure 4.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of the RdRp amino acid sequence of PBVs. Tree was constructed using the LG + G amino acid model using RAxML, with the autoMRE flag, which enables a posteriori bootstopping analysis. Tree was midpoint rooted for purposes of clarity. Only bootstrap values >70% are shown except at branches and clusters including the novel bat viruses. Bars indicate amino acid substitutions per site. Red strains: sequences from this study; orange strains: Genogroup I PBVs; green strains: genogroup II PBVs; light purple and blue: unclassified PBVs that use standard genetic code; purple: PBV-like viruses that use alternative genetic code; strains with asterisk: PBVs that use alternative genetic code in Genogroup II. (B) PCA based on the genetic code usage of viral and mitochondrial genomic sequences. Graphs represent separation of groups using the most influential factors and points represent values for individual sequences. P11-300, P11-378, P14-90, P15-218, and P16-366 are the novel Cameroonian PBVs.