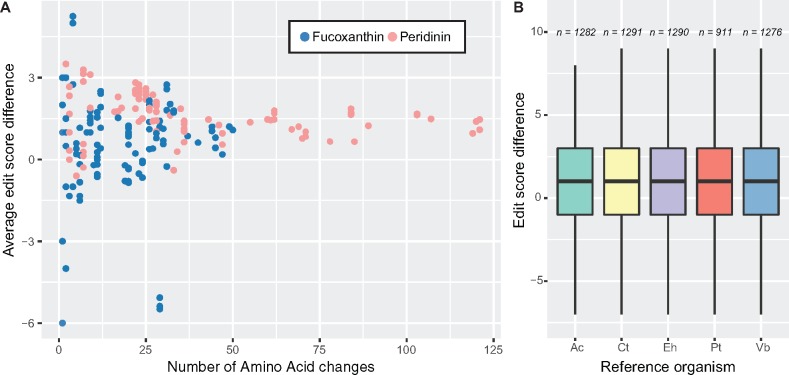
Fig. 7.
—Summary of corrective editing. This figure highlights the overall corrective effect of editing to result in amino acids that are more similar to their homologues in orthologues from organisms that do not undergo RNA editing than those originally encoded in the genomic sequence. (A) Scatter plot of the relationship between the number of editing events and the average editing score for each gene. (B) Boxplots showing that the corrective effect is independent of choice of reference organism; n denotes sample size (number of events). Abbreviations: Ac, Amphidinium spp.; Ct, Chrysochromulina tobin; Eh, Emiliania huxleyi; Pt, Phaeodactylum tricornutum; Vb, Vitrella brassicaformis; Km, Karenia mikimotoi; Kv, Karlodinium veneficum; Pl, Pyrocystis lunula; Sm, Symbiodinium minutum.