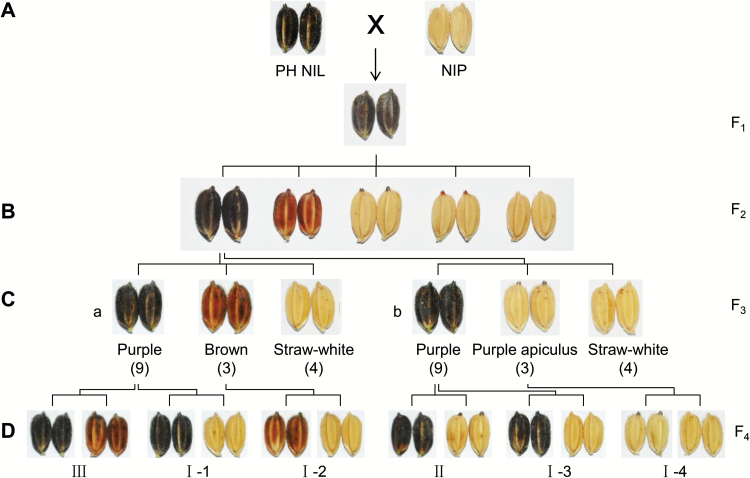
Fig. 1.
Inheritance of hull coloration. (A) Purple hulled PH NIL was crossed with NIP; the hull color of F1 was purple. (B) The F2 population segregated into five phenotypes (purple hull, brown hull, purple apiculus, brown apiculus, and straw-white hull). (C) F3 populations ‘a’ and ‘b’ segregated in 9:3:4 ratios but with different phenotypes. The line F3-a shows the separation of different colors and F3-b shows the separation of the pigmentation part. In line F3-a, hull color segregated as purple, brown and straw-white. In line F3-b, color segregated as purple hull, purple apiculus, and straw-white hull. (D) F4 segregating lines were obtained from F3 individuals as indicated. Six single gene segregation patterns were confirmed. Lines I-1, -2, -3, and -4 segregated colored (purple or brown) and straw-white phenotype, implying color is controlled by a chromogen gene. Line II segregated in a tissue-specific pattern, implying regulation by a tissue-specific pigmentation gene. The segregation in line III indicated that there is an activator for purple color. The phenotypic data are provided in Supplementary Table S4.