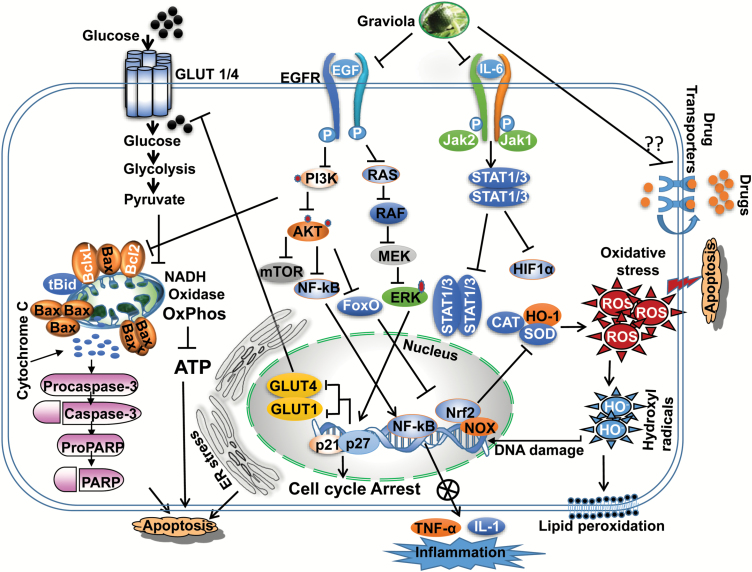
Figure 1.
Possible anticancer mechanisms of graviola. Graviola induced apoptosis by loss of MMP and activation of caspases. Suppression of EGFR and JAK signaling leads to blockade of the PI3K, RAS and STAT pathways, respectively, culminating in decreasing cell viability and metabolic catastrophe by down-regulating HIF-1α, GLUT1, GLUT4, expression, associated with decreased glucose uptake and cell cycle arrest in human cancer cells. Graviola inhibits NF-κB mediated TNF-α and IL-1 expression to control inflammation. Graviola increases ROS generation by effecting the expression of catalase (CAT), SOD and heme-oxygenase (HO-1) expression. Graviola also kills the drug-resistant cells possible by modulating multidrug-resistant export proteins.