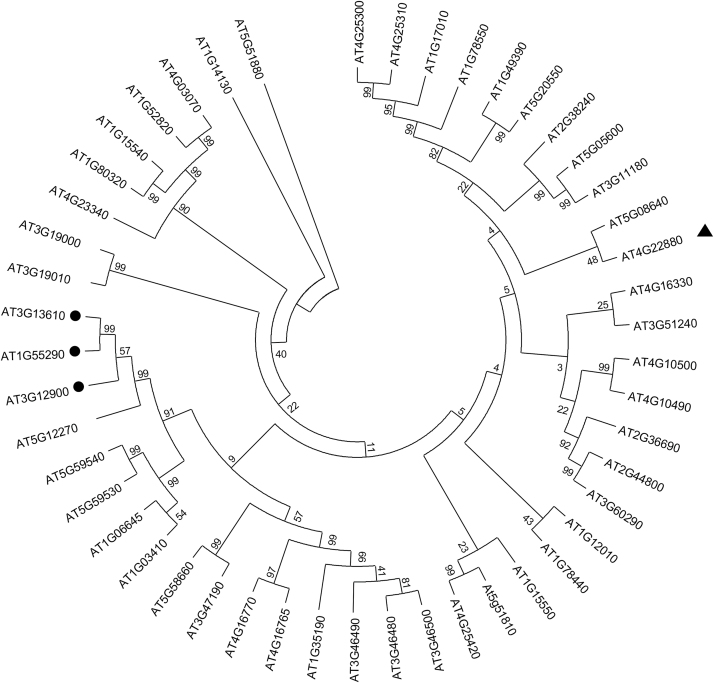
Fig. 1.
Nucleic acid sequence-based tree. The phylogenetic analysis was performed on available nucleic acid sequences of genes encoding 2-oxoglutarate (2OG)- and ferrous iron Fe2+-dependent dioxygenase (2OGD) from the Arabidopsis genome. The phylogenetic tree was made using MEGA 6 software. Black circles indicate genes (At3g13610 and At1g55290) encoding enzymes involved in scopoletin biosynthesis (F6ʹH1 and F6ʹH2 respectively), and their closest homologue based on the nucleic acid sequences, a gene (At3g12900) encoding a dioxygenase of unknown biological function (characterized in this study as S8H). The black triangle indicates a gene (At4g22880) encoding the anthocyanidin synthase (ANS) enzyme. Nucleic sequences downloaded from TAIR were selected based on the presence of sequences coding for Fe-binding (His-X-Asp-X-His) and 2OG-binding (Arg-X-Ser) motifs (Wilmouth et al., 2002).