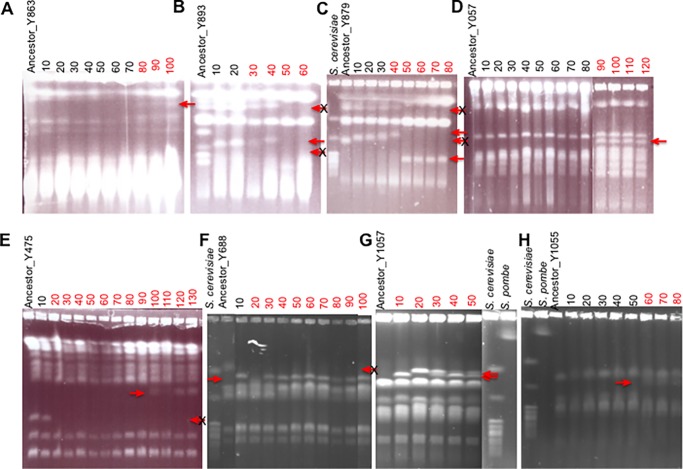
Fig 4. Evolutionary trajectories based on electrophoretic karyotypes.
The figure shows chromosomal bands separated by PFGE using a CHEF Mapper XA PFGE apparatus (Bio-Rad). To determine karyotypes, overnight cultures from each of the frozen samples stored after every 10 passages were used. Preparation of chromosomal plugs for PFGE was done by standard methods as reported [40]. Plugs were run using a multistate program for 110 h (Block 1, 25 h at 1.5 V/cm with a 2, 700 s pulse time and an angle of 53°; Block 2, 25 h at 1.5V/cm with a 2, 200s pulse time and an angle of 60°; Block 3, 30 h at 2 V/cm with a 1.500 s pulse time and an angle of 60°; and Block 4, 30 h at 2.5 V/cm with a 500-s pulse time and an angle of 60°) at a constant temperature (14°C) [52]. The gels were stained with ethidium bromide before photographing. Most ancestral strains used in this study are completely sequenced to be used as standards to estimate the sizes of novel bands based electrophoretic migration distance regression curve. In some cases, S. cerevisiae (S288c) and Schizosaccharomyces pombe (SJA148) were used as standards. Strains that underwent a rearrangemnt event are labelled in red. Bands that were not found on the respective ancestral lane are shown by a red arrow whereas those that were lost are shown by a cancelled red arrow. D. anomala (Y863), B. custercianus (Y893), D. bruxellensis (Y879), L. kluyveri (Y057) [16], C. glabrata (Y475), L. thermotolerans (Y688), K. nonfermentans (Y1057) and T. pretoriensis (Y1055).