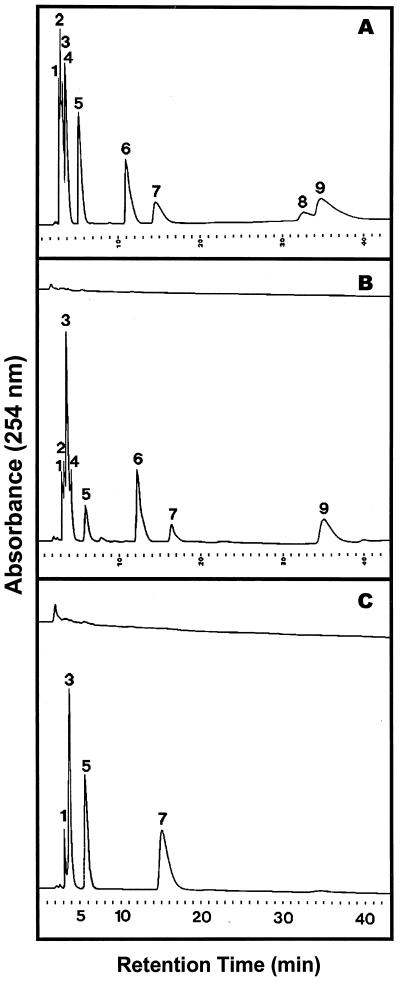
Figure 5.
Elution profile of ribonucleoside monophosphates after hydrolysis of yeast RNA with purified RNase LE and purified tomato extracellular phosphodiesterase. Enzymatic hydrolysis of RNA and HPLC separation of monomeric products on Octadecyl-Si 100 were performed as described in “Materials and Methods.” Shown are elution profiles of standard compounds (A), monomeric products of RNA hydrolysis with RNase LE for the zero-time control (B, upper tracing) and after 6 h of reaction (B, lower tracing), and monomeric products of RNA hydrolysis with extracellular phosphodiesterase for 6 h (C, upper tracing) and with RNase LE for 6 h followed with extracellular phosphodiesterase for 3 h (C, lower tracing). Peak identities: 1, 3′-CMP/2′-CMP; 2, 2′:3′-cyclic CMP; 3, 3′-UMP/2′-UMP; 4, 2′:3′-cyclic UMP; 5, 3′-GMP/2′-GMP; 6, 2′:3′-cyclic GMP; 7, 3′-AMP; 8, 2′-AMP; 9, 2′:3′-cAMP.