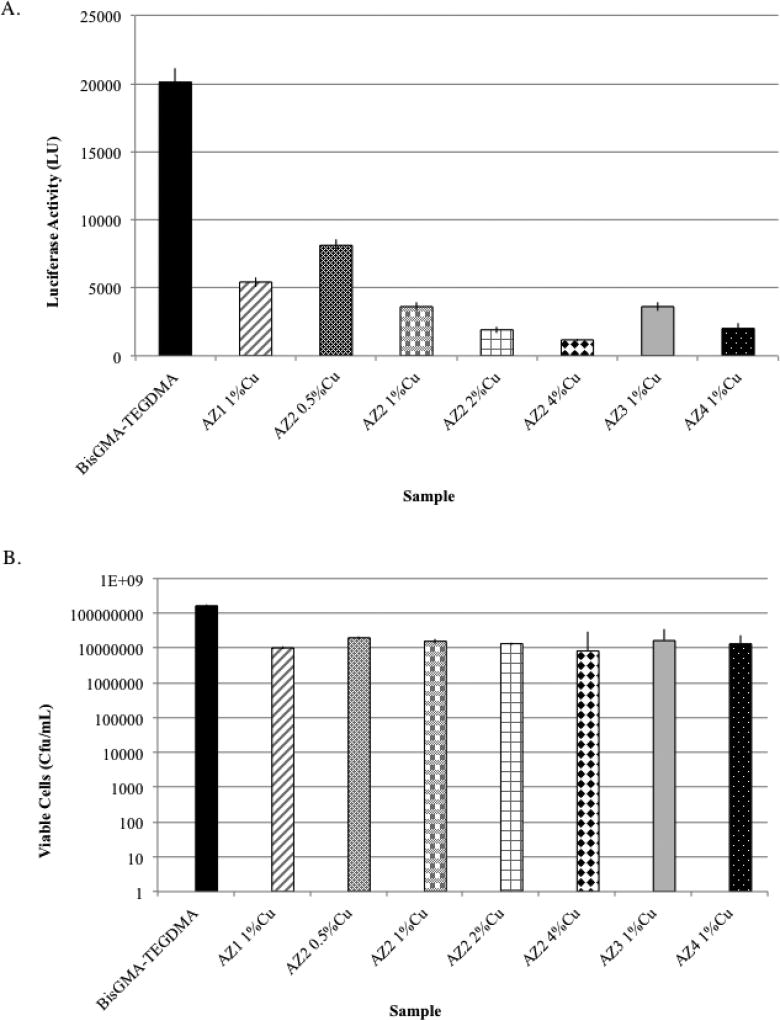
Fig. 2.
Evaluation of bioburden on BisGMA-TEGDMA and novel CuAAC-based resins having varying Azide monomers and differing concentrations of CuCl2 in AZ-2 containing resins. Non-disruptive analysis of biofilm bioburden using luciferase measurements (A) indicated a statistically significant reduction (p <0.05) in the luminescence observed on the novel CuAAC-based discs compared to BisGMA-TEGDMA-based resins (n=12 discs), suggesting a reduction in the bioburden associated with the biofilms grown on the CuAAC resin-based discs. Disruptive analysis of biofilms (B) from BisGMA-TEGDMA and CuAAC resin-based discs (n=12) indicated a significant reduction (p <0.05) in the number of bacteria recovered from biofilms on each novel resin when compared to biofilms associated with the BisGMA-TEGDMA.