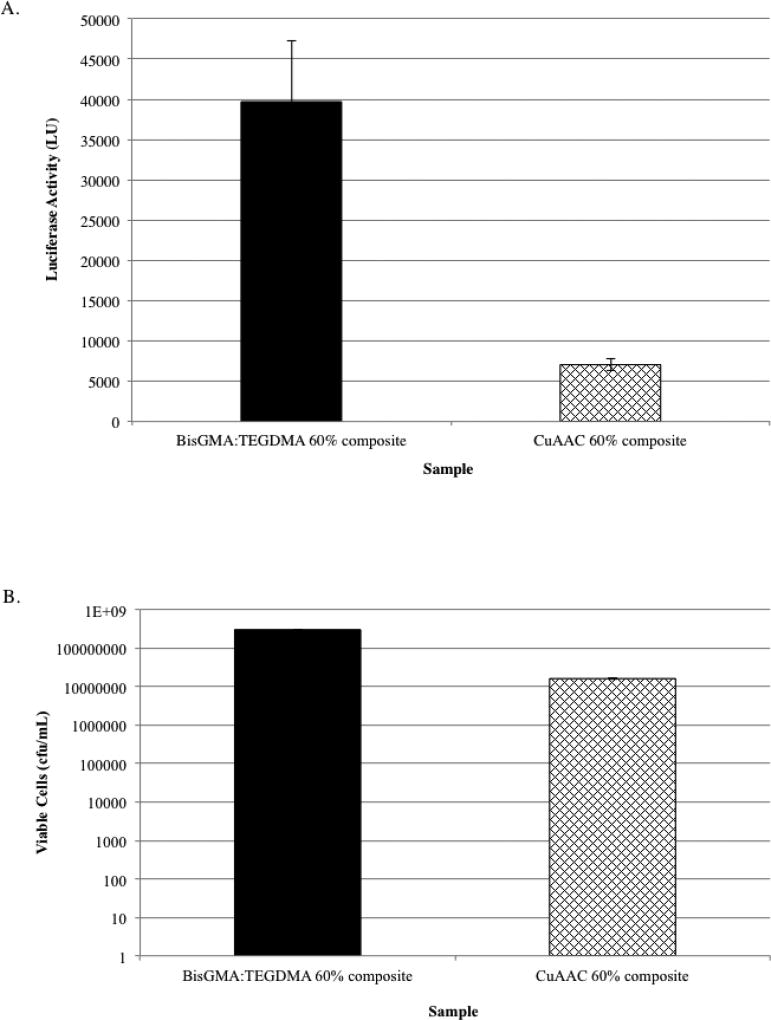
Fig. 3.
Evaluation of bioburden on novel CuAAC-based and BisGMA-TEGDMA-based composites using non-disruptive (A) and disruptive analyses (B). Nondisruptive luciferase analysis (A) of S. mutans firefly biofilm grown on CuAAC 60% composite discs (containing AZ-2 diazide, trialkyne (a mole ratio of 1:1 to N3:alkyne), with 2 mole percentage of CuCl2[PMDETA] per functionality, 2 mole percentage of CQ and 60-weight percentage of alkyne-functionalized microfillers (Schott, 0.4 µm)) and on BisGMA-TEGDMA 60% composite discs (n=12) (containing BisGMA-TEGDMA (70:30 weight ratio) with 2-weight percentage of CQ having 60-weight percentage of methacrylated microfillers (Schott, 0.4 µm)) indicated a statistically significant reduction (p >0.05) in luminescence, indicating a reduced bioburden on CuAAC composite discs. Disruptive analysis (B) of CuAAC 60% composite discs and BisGMA-TEGDMA 60% composite discs also showed a significant reduction (p <0.05), having nearly a 2-log reduction in bioburden on CuAAC based composites.