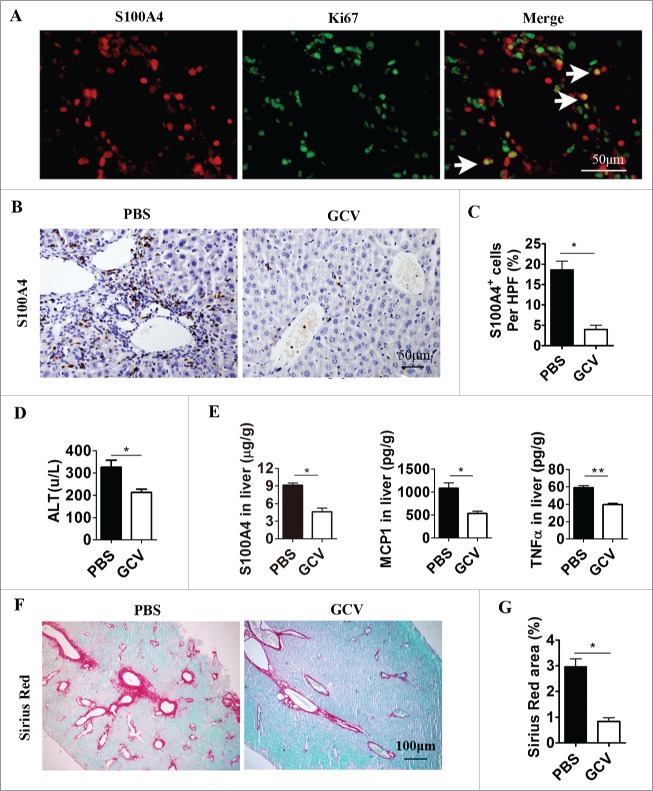
Figure 3.
Selective depletion of S100A4+ cells attenuates anti-CD137 mAb-induced liver injury and liver fibrosis. S100A4-TK mice (n = 5) were treated with 100 µg 2A on day 1 and then injected with GCV or PBS on days 1, 3, 4, 6 and 7. The treatment was repeated for 4 weeks. (A) Proliferating S100A4+ cells in 2A-treated livers from S100A4-TK mice were stained for both S100A4 (red) and Ki67 (green). Arrows indicate double-positive cells (yellow). Scale bar, 50 μm. (B) Groups of S100A4-TK+ mice (n = 5 per group) were left untreated or treated with GCV to deplete S100A4+ cells, and liver sections were stained for S100A4. Scale bar, 50 μm. (C) Percentage of S100A4-positive cells. *p < 0.05. (D) Serum ALT levels of S100A4-TK+ mice treated with or without 2A. *p < 0.05. (E) The content of S100A4, MCP-1, and TNF-α protein in the liver homogenates of PBS or GCV-treated TK+ mice was measured by CBA or ELISA. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (F) Groups of S100A4-TK+ mice were left untreated or treated with GCV, and liver sections were stained with Sirius Red. Scale bar, 100μm. (G) Quantification of Sirius Red areas in the liver sections. *p < 0.05.