Figure 8.
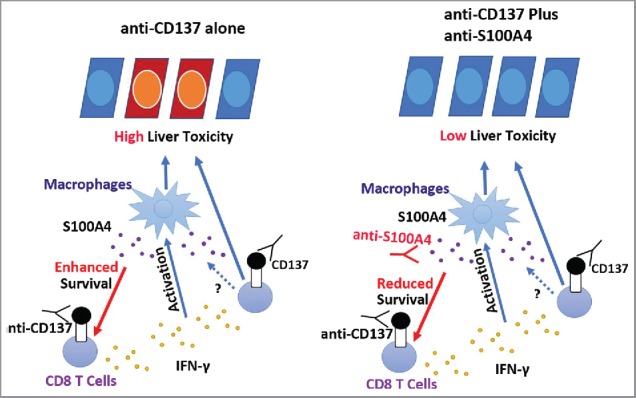
The role of S100A4 in anti-CD137-induced liver toxicity. CD8+ T cells, mainly the memory T cells, are activated by the anti-CD137 antibody in the liver and secrete large amounts of IFNγ, leading to the activation of macrophages and liver toxicity. During this process, large amounts of S100A4 are produced specifically inside of the liver and enhance CD8+ T cell survival, further amplifying the liver damage. Targeting S100A4 with an S100A4 blocking antibody affects CD8+ T cell survival and causes minimal liver toxicity. Similar effects could also be obtained by S100A4 deficiency or depletion of S100A4-positive macrophages.
