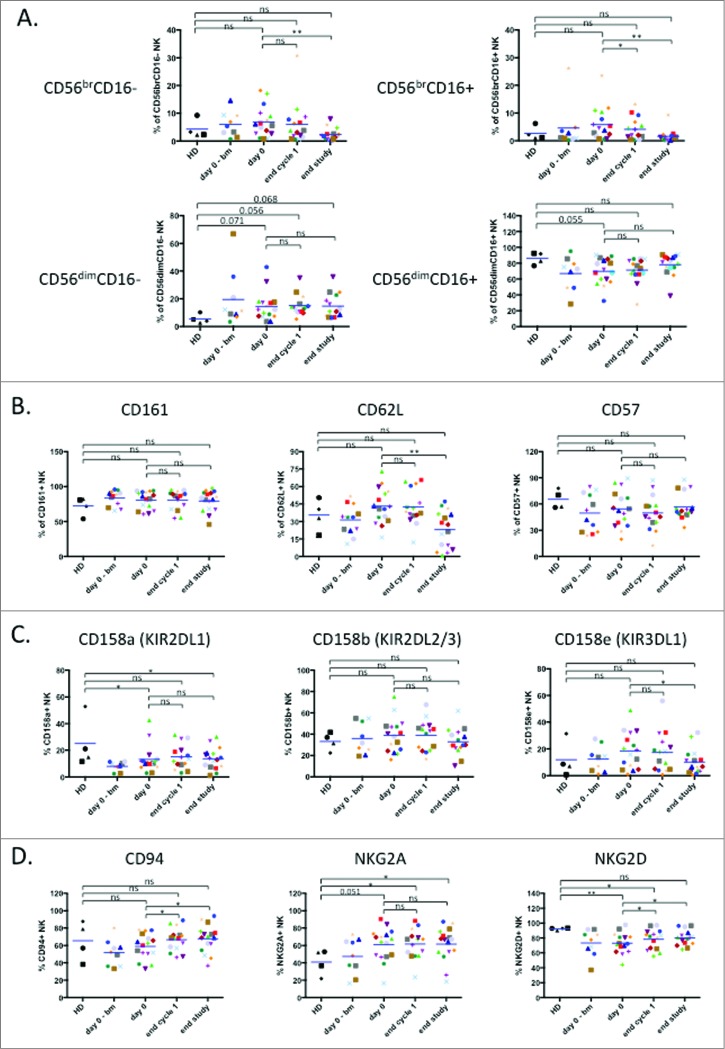
Figure 2.
Treatment induces maturation of the immature NK cell population. (A) Analysis of NK cell subpopulations based on level of CD56 and CD16 expression that divides NK cells in 4 subpopulations: CD56brCD16− (top, left panel), CD56brCD16+ (top, right panel), CD56dimCD16− (bottom, left panel) and CD56dimCD16+ (bottom, right panel). (B) Assessment of NK cell maturation status determined by expression of the maturation markers CD161, CD62 L and CD57. (C) Expression of several KIR receptors on healthy donor and patient NK cells: CD158 a (KIR2DL1), CD158b (KIR2DL2/3) and CD158e (KIR3DL1). (D) Expression of the inhibitory heterodimer complex NKG2 A/CD94 and the activating receptor NKG2D. Patient: n = 16, healthy donor: n = 4. Significance was determined by paired t-test between day 0 versus following time-points, and one-way ANOVA between HD and patients at every time-points with * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01 and *** p ≤ 0.001.