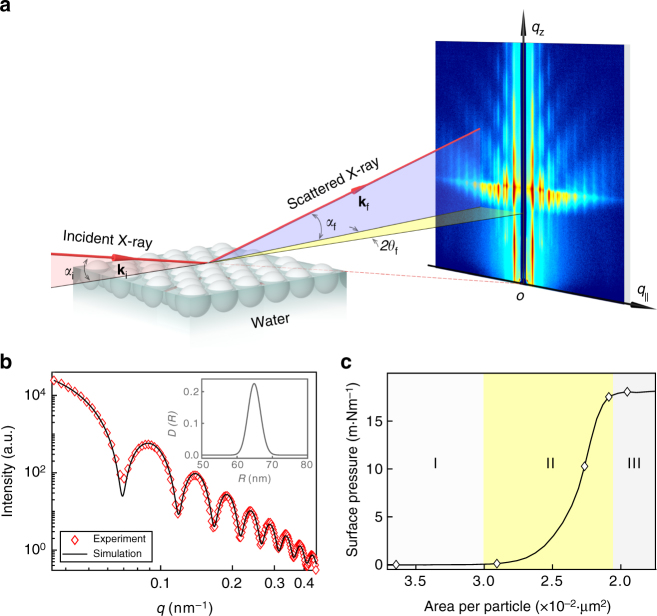
Fig. 1.
GISAXS experimental set-up and sample characterizations. a The schematic illustration of the GISAXS experimental geometry. ki and kf are the incident and scattered wave vectors, respectively, yielding the wavevector transfer (i.e., the reciprocal space vector) ; αi is the incident angle of X-ray beam; and αf are the azimuthal and exit scattering angles, respectively. A long beamstop is installed to protect the detector from the reflected and direct beams. b The SAXS data (red diamonds) for PNSs dispersed in aqueous solution and their theoretical fit (black solid line) using the spherical form factor with its polydispersity described by the Schultz distribution. Inset: the size distribution of the PNSs. c The real-time surface pressure-particle area isotherm for the self-assembly of PNSs adsorbed at the air/water interface of the LB trough taken during the in situ GISAXS experiment