Fig. 2.
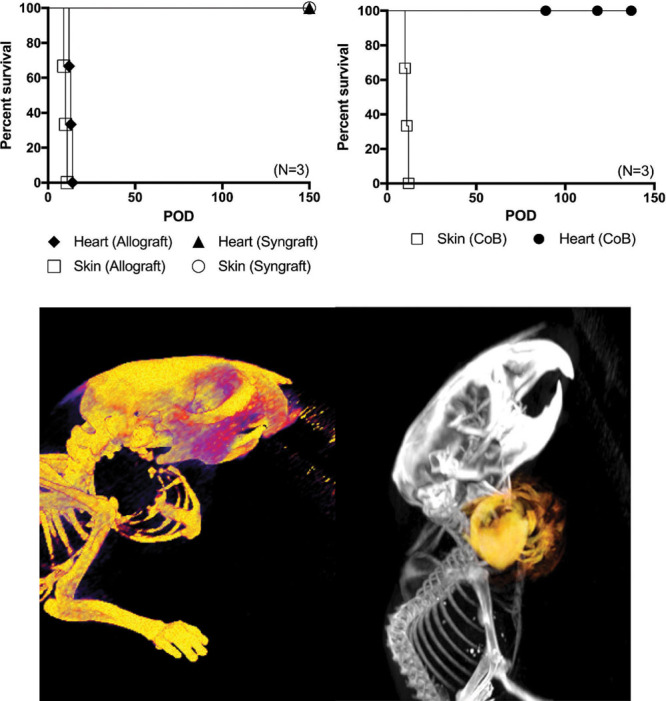
Kaplan–Meier survival curve. Syngeneic (N = 5) versus allogeneic (N = 3) en bloc chest wall, thymus, and heart VCA (A). Although syngeneic grafts show long-term survival of both skin and heart components clinically and histologically, rejection of fully H2-mismatched grafts appear early with skin component rejection at an average of 10 days and heart component at an average of 13 days after transplantation. Survival of en bloc chest wall, thymus, and heart allograft components using costimulation blockade (N = 3). Skin component rejection occurs as early as 9 days after transplantation (average: 10 ± 1 d), whereas survival of the heart component and other tissue components is prolonged with costimulation blockade (B). Micro-computed tomography (CT) image of the chest wall recipient from a lateral–dorsal perspective showing graft inset location at the lateral aspect of the right neck ([C], left). Overlay of micro-CT and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showing both contours of the chest wall and the heart as a VCA ([C], right).
