Fig. 1.
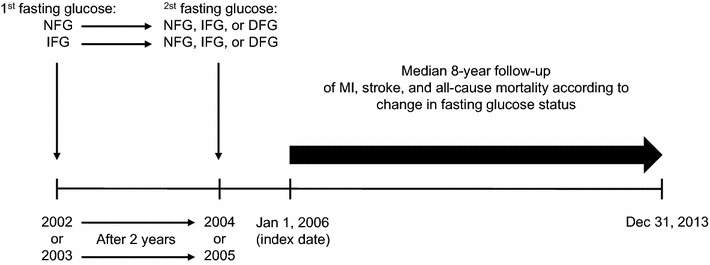
Timeline of the study design. Subjects without diabetes and cardiovascular disease performed 2-year fasting serum glucose examination. The first fasting glucose status was categorized into two groups, normal fasting glucose [(NFG), fasting serum glucose: < 100.0 mg/dL] and impaired fasting glucose [(IFG), fasting serum glucose: 100.0–125.9 mg/dL] (individuals with more than 126 mg/dL were excluded). The second fasting glucose status was categorized into three groups, NFG, IFG, and diabetic fasting glucose [(DFG), fasting serum glucose: ≥ 126.0 mg/dL]. Accordingly, six categories based on the change in fasting glucose level were followed up during 8 years for determining the risk of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and all-cause mortality
