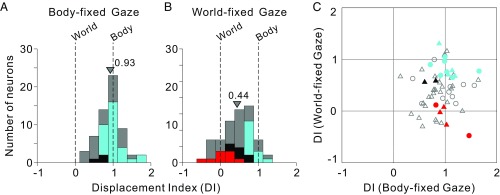
Fig. 3.
Summary of spatial reference frames for vestibular heading tuning in VIP, as quantified by the DI. (A and B) DI values of 1 and 0 indicate body- and world-centered tuning, respectively. Data are shown for both body-fixed gaze (A; n = 60) and world-fixed gaze (B; n = 61) conditions. Cyan and red bars in A and B represent neurons that are statistically classified as body- and world-centered, respectively (see Methods for details). Black bars represent neurons that are classified as intermediate, whereas gray bars represent neurons that are unclassified. Arrowheads indicate mean DI values for each distribution. Mean values of the DI distributions for monkeys F and X were not significantly different (body-fixed gaze: P = 0.06; world-fixed gaze: P = 0.28, t tests); thus, data for A and B were pooled across monkeys. (C) Scatter plot comparing DI values for the body- and world-fixed gaze conditions. Circles and triangles denote data from monkeys F and X, respectively. Colors indicate cells classified as body centered in both conditions (cyan), intermediate in both conditions (black), or body-centered in the body-fixed gaze condition but world-centered in the world-fixed gaze condition (red). Open symbols denote unclassified neurons (Table S1).