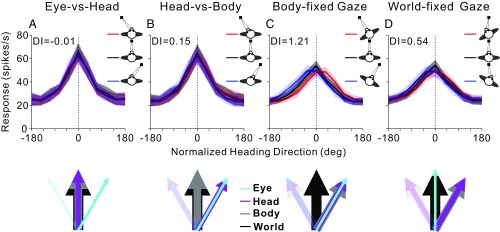
Fig. 6.
Summary of vestibular heading representation in VIP. Average normalized heading tuning curves and DI values for data from Chen et al. (19) (A and B) and for the current data (C and D). Colored lines and error bands indicate the mean firing rate ± SEM. Vertical dotted lines show the direction around which tuning curves are aligned (see SI Methods for details). The colored arrows below each graph indicate the direction of reference frames in each condition. The direction of the world reference (thick black arrow) is the same in all schematics. In A (eye vs. head), eye position (cyan arrows) was varied, while head and body positions (magenta and gray arrows) were kept constant. In B (head vs. body), eye and head positions changed together, while body orientation was fixed. In C (body-fixed gaze), eye, head, and body all varied together. In D (world-fixed gaze), head and body changed, while eye position was fixed in the world.