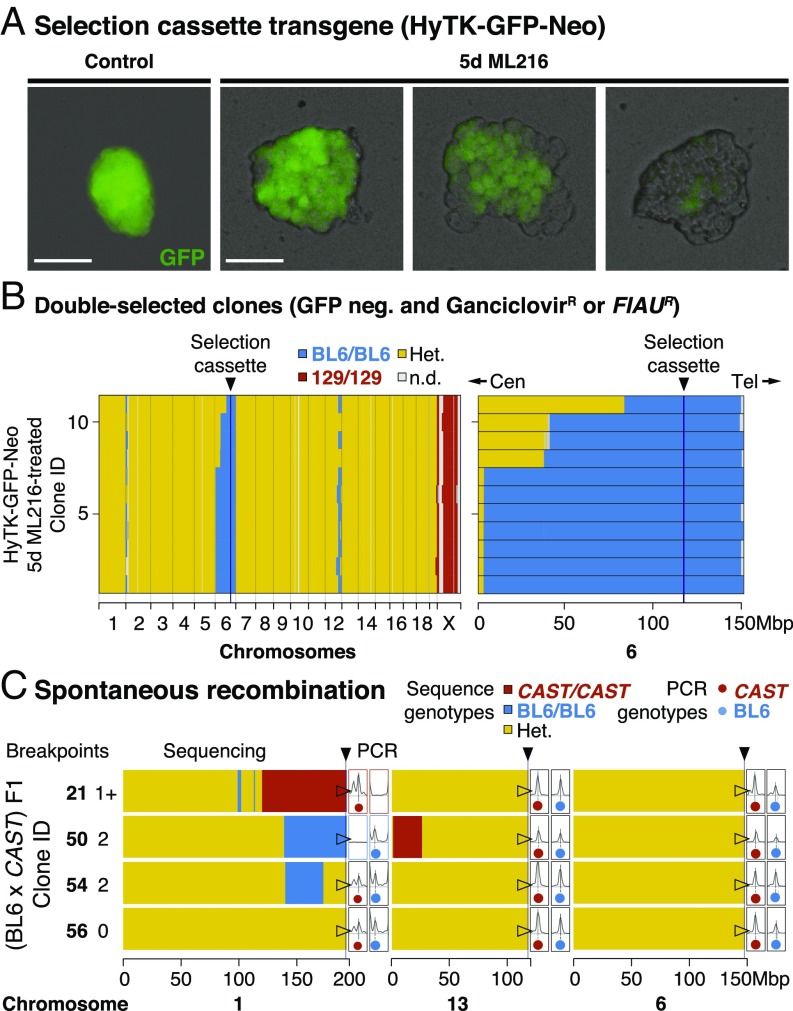
Fig. 2.
Widespread IVR across a range of evolutionary divergence. (A) Selection cassette transgene (HyTK-GFP-Neo). ES cell colonies displayed mosaic GFP expression within a colony when cultured with ML216, but not under control conditions, consistent with homologous recombination and loss of GFP through IVR. Recombination between homologous chromosomes could result in daughter cells with two wild-type (BL6 allele; dark) or transgenic copies (129 allele; bright). Early recombination events followed by random cell loss during clonal expansion could produce completely dark colonies. (Scale bars: 100 µm.) (B) Double-selected clones. After expansion under negative selection against the transgene (both ganciclovir and FIAU kill cells expressing HyTK), 11 ganciclovir-resistant and GFP-negative colonies were whole-genome sequenced. Selection favored loss of transgene (homozygous BL6/BL6 genotypes) at distal chromosome 6. In contrast to normal meiotic recombination (averaging one or more cross-overs per chromosome pair), mitotic recombination typically affected only a single chromosome pair: Much of the genome remained heterozygous (Het.; yellow), with the exception of the transgene-carrying chromosome 6 (mostly BL6/BL6; blue), the single 129 chromosome X (male; 129; red), and at tips of certain chromosomes (e.g., chromosomes 1 and 12). Mitotic recombination events converted genotypes telomeric to the breakpoint toward homozygosity (LOH; yellow to blue). Cen, centromere; n.d., not determined; Tel, telomere. (C) Spontaneous recombination. IVR also occurred in cells carrying divergent genomes with no transgenes. (BL6 × CAST) F1 hybrid ES cells were treated with ML216 and screened by PCR genotyping at diagnostic telomeric markers. Selected clones (two recombinant and control clones each) were whole-genome sequenced, showing recombination events toward both homozygous genotypes, consistent with PCR genotype screening results (total breakpoints per clone ranged from zero to two). Additional recombination events were also recovered, even though the chromosome 1 telomeric marker remained heterozygous (clone 54). These clones also carried nonrecombined chromosomes (e.g., chromosome 6; fully heterozygous; yellow).