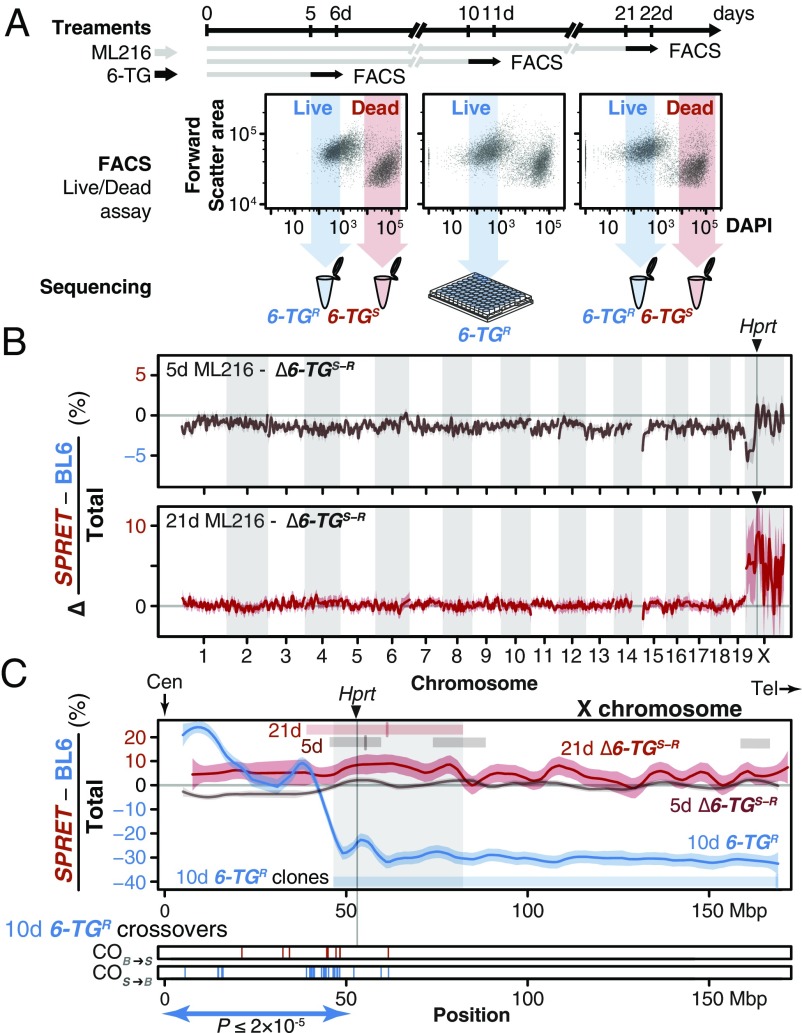
Fig. 3.
In vitro genetic mapping of variation in 6-TG susceptibility between divergent species. (A) A female ES cell line S18 derived from a M. spretus and BL6 F1 interspecific hybrid was treated with ML216 (25 µM) and subjected to the antimetabolite 6-TG for 1 d before FACS. ES cells were evaluated for viability based on DAPI exclusion. Resistant and susceptible (6-TGR and -TGS) subpopulations were gated conservatively (shaded arrows) and pooled for sequencing. Individual clones from the 10-d ML216 treatment were cultured and whole-genome sequenced. (B) An excess of SPRET contribution on chromosome X between the 6-TGR and -TGS pools suggested that a single locus conferred 6-TG susceptibility. Allele counts were shown as the difference in SPRET bias between the 6-TGs and the 6-TGR samples (as an internal ML216 treatment control) after 5-d (brown) and 21-d (red) ML216 treatment (mean differential SPRET bias ± SEM in megabase windows). In both cases, the genome-wide peak window contains the Hprt gene with the SPRET allele showing significantly increased susceptibility. (C) Detailed view of chromosome X, showing differential SPRET bias for the 5-d (brown) and 21-d (red) ML216 treatment as described above. In addition, 6-TGR clones following 10-d ML216 treatment were sequenced to determine recombination breakpoints. In contrast to the differential bias toward SPRET observed in the susceptible 5- and 21-d ML216 samples, the raw SPRET bias in the solitary 6-TG–resistant sample showed an opposite skew toward BL6 in the 10-d ML216-treatment (blue). Regions deviating from 0 (thus showing bias) after local smoothing in each sample are shown as bars with mark showing maximum skew. Together, they define a common region (shaded) on chromosome X containing Hprt. Cross-overs in individual 6-TGR clones (10-d ML216 treatment) recombined significantly more likely in the SPRET-to-BL6 direction (S > B = 37; B > S = 5; P ≤ 2 × 10−5) between the centromere (Cen) and Hprt, consistent with strong selection favoring the BL6 Hprtb allele. In contrast, only three additional cross-overs were detected telomeric to Hprt. Tel, telomere.