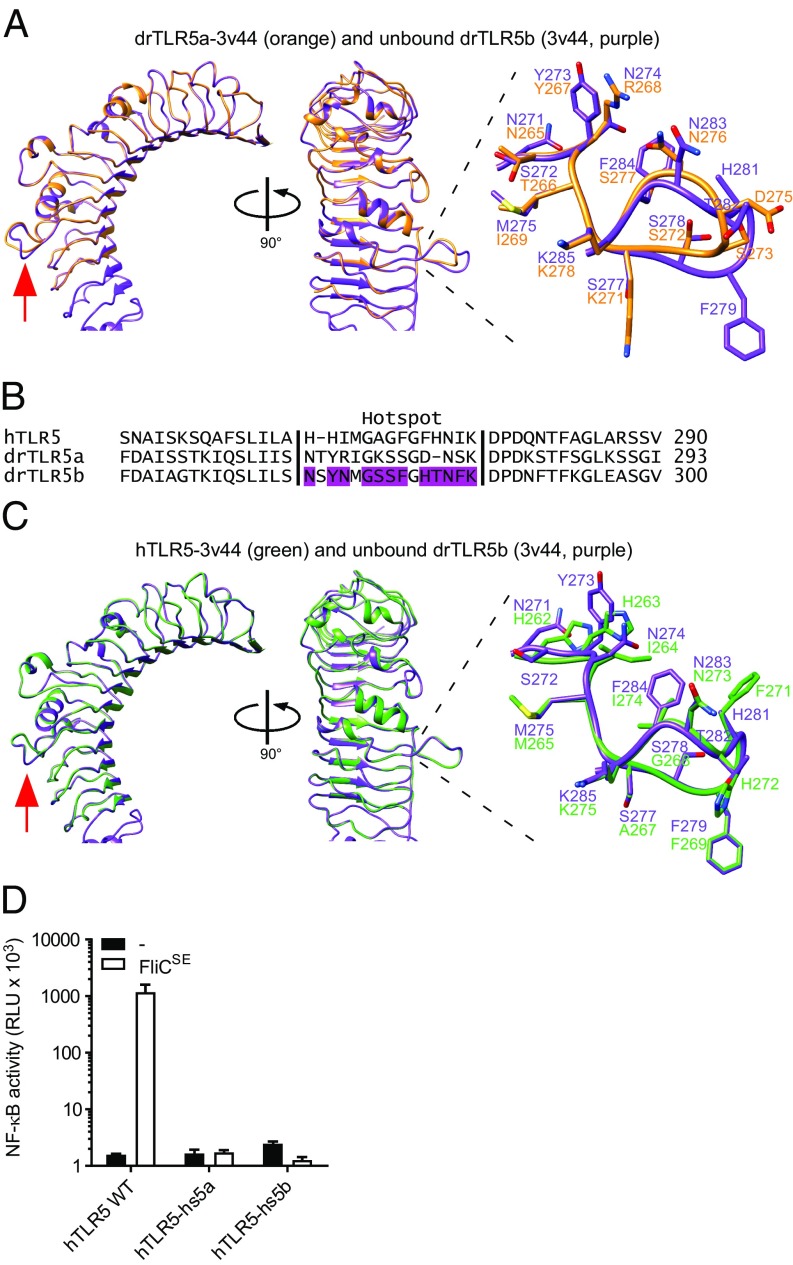
Fig. 5.
Structural modeling and functionality of the flagellin-binding hotspot in hTLR5, drTLR5a, and drTLR5b. (A) Superposition of unbound drTLR5b (PDB ID: 3v44; purple) and a model of drTLR5a based on 3v44 (drTLR5a-3v44; orange). The red arrow indicates the flagellin-binding hotspot that forms a loop between LRR9 and LRR10. (B) Alignment of the putative flagellin-binding hotspot of hTLR5 and drTLR5a with drTLR5b. Purple-colored residues in drTLR5b are involved in flagellin binding (see ref. 19). (C) Superposition of unbound drTLR5b (PDB ID: 3v44; purple) and a model of hTLR5 based on 3v44 (hTLR5-3v44; green). (D) HeLa-57A cells transfected with WT hTLR5 (hTLR5 WT), hTLR5 containing the hotspot of drTLR5a (hTLR5-hs5a), or the hotspot of drTLR5b (hTLR5-hs5b) were stimulated (5 h) with vehicle (–) or 1 µg mL−1 FliCSE. Data show NF-κB activity represented by luciferase activity in RLUs. Values are the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in duplicate.