Fig. 3.
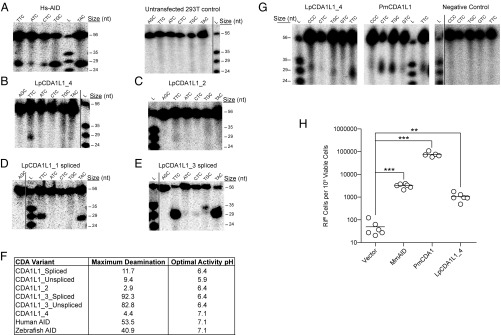
Cytidine deamination activity of CDA1L1 variants. (A) Representative alkaline cleavage gel of human AID (Hs-AID) activity using different substrates, each containing the target (d)C in varying nucleotide sequence contexts at various temperatures [results are shown for assay conducted at 37 °C, pH 7.1 (cf. SI Appendix, Fig. S9A, Middle)]. A representative negative control deamination assay using extracts of untransfected 293T cells is shown at Right. (B) Representative alkaline cleavage assay of LpCDA1L1_4. (C–E) Representative alkaline cleavage assays for LpCDA1L1_2, LpCDA1L1_1, and LpCDA1L1_3, the latter two proteins in spliced versions (cf. SI Appendix, Fig. S4). The enzyme assays in B–E were conducted at 22 °C in phosphate buffer (pH 6.4), except for LpCDA1L1_4, which was tested at pH 7.1. (F) Summary table indicating the enzymatic activities of human AID and Lampetra planeri CDA1L1 proteins (cf. SI Appendix, Fig. S9). (G) Representative alkaline cleavage assay gels of LpCDA1L1_4 (Left) and PmCDA1L1 (Middle) purified as N-terminally tagged GST fusion proteins expressed in E. coli. The proteins were incubated at 14 °C with different bubble substrates containing the target (d)C in varying nucleotide sequence contexts, in phosphate buffer (pH 7.1). The Right gel depicts the negative control experiment wherein substrates were incubated with buffer alone and no enzyme, under the same conditions. (H) Mutagenic activities of the mouse AID (MmAID), PmaCDA1, and LpCDA1L1_4 in bacteria containing a mutation in the ung-1 gene that encodes for uracil-DNA glycosylase 1 (UDG1), which prevents repair of deaminase-induced C-to-U DNA transitions. Activity was measured as the number of rifampicin-resistant (RifR) colonies per 109 viable cells (number of ampicillin-resistant colonies) (53). Deaminase activities were evaluated against the vector control using an unpaired Student’s t test with Welch’s correction. ***P < 0.0001, **P < 0.0021. In this assay, LpCDA1L1_1 and _2 also showed significant deaminase activities. Some display items were combined from different parts of the same autoradiographic films; the splice sites are indicated by solid lines.