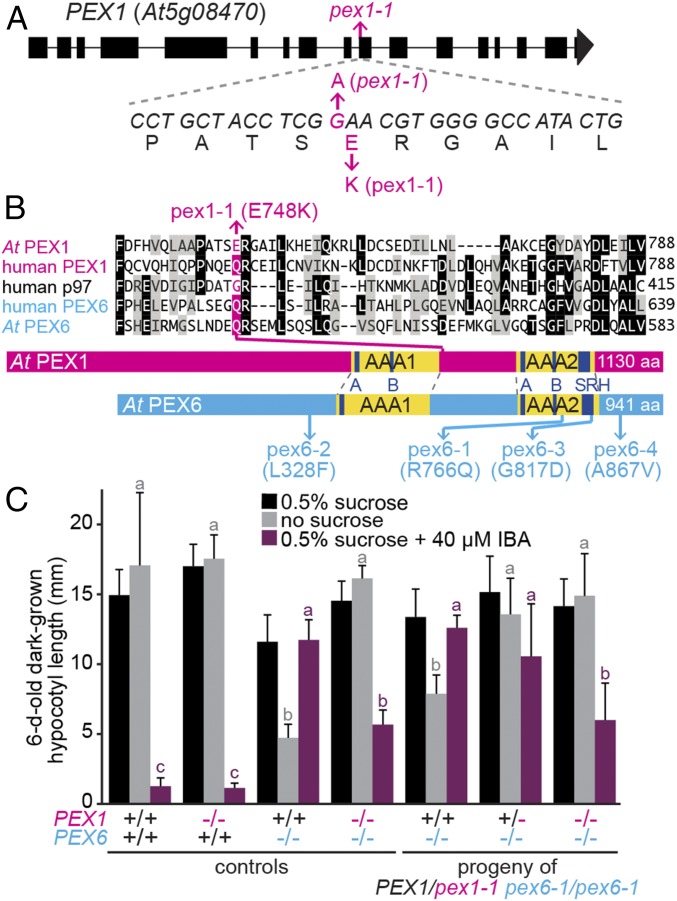
Fig. 1.
pex1-1 identification. (A) PEX1 gene diagram showing exons (rectangles), introns (lines), and the location of pex1-1, a G-to-A transition that yields a Glu748-to-Lys substitution. (B) Partial alignment of Arabidopsis and human PEX1 and PEX6 and human p97 (a related ATPase) above protein schematic illustrations depicting the locations of pex1-1 and previously described pex6 missense alleles (35, 37, 44). The complete AAA domains are in yellow, with the Walker A (A), Walker B (B), and second region of homology (SRH) domains highlighted in navy blue. (C) pex1-1 is semidominant; the PEX1/pex1-1 heterozygote partially suppresses pex6-1 sucrose dependence and IBA resistance. Seedlings were grown on the indicated media for 1 d under yellow-filtered light before moving to darkness for 5 d. Bars indicate mean hypocotyl lengths, and error bars indicate SD (n ≥ 13 except for pex6-1 PEX1 and pex6-1 pex1-1 from the segregating parent, for which n ≥ 5). Means not sharing a letter above the bar are significantly different as determined by one-way ANOVA (P < 0.001).