Fig. 2.
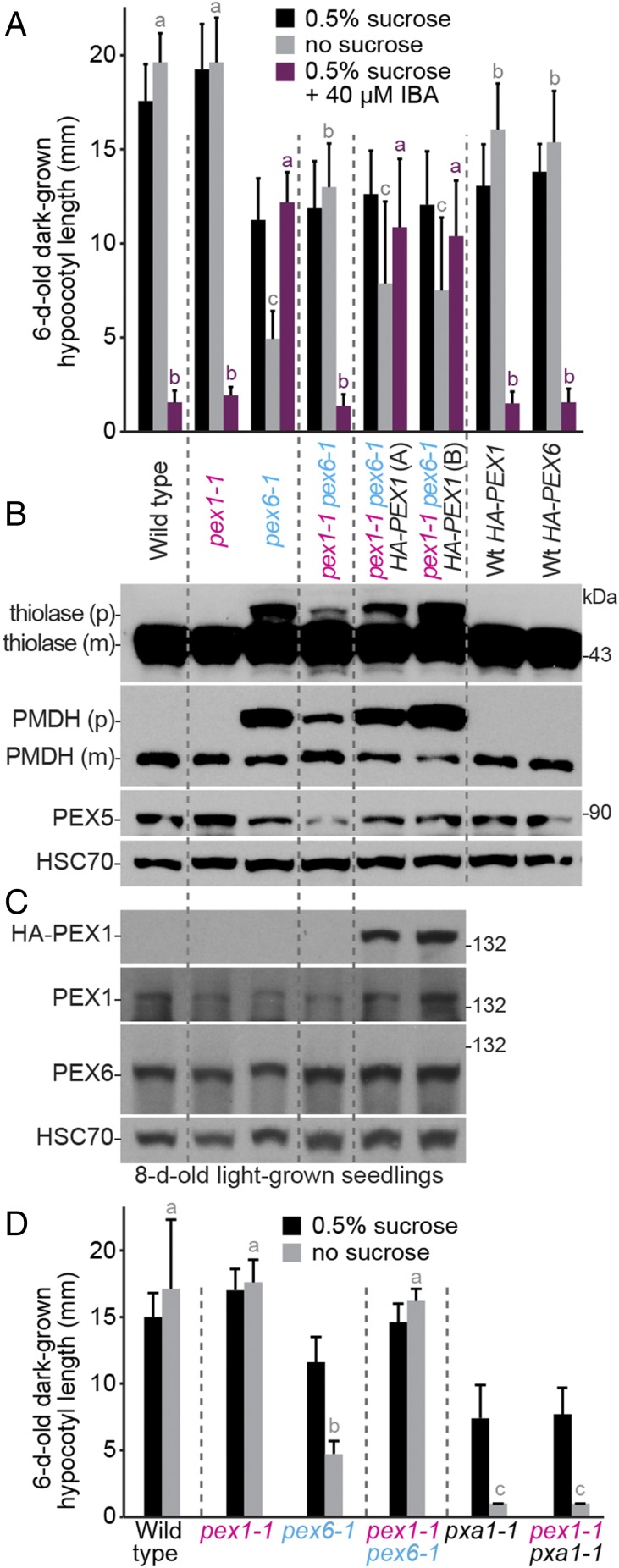
Overexpressing PEX1 in pex1-1 pex6-1 phenocopies pex6-1 defects; pex1-1 does not restore pxa1-1 growth. (A) Expressing HA-PEX1 increases resistance to the inhibitory effects of IBA and hypocotyl elongation dependence on exogenous sucrose of dark-grown pex1-1 pex6-1 seedlings. Two independent pex1-1 pex6-1 35S:HA-PEX1 lines (A and B) are shown. Seedlings were grown as in the legend to Fig. 1C. Bars indicate mean hypocotyl lengths (n ≥ 13), and error bars indicate SD. (B) PTS2-processing defects of light-grown pex1-1 pex6-1 seedlings are worsened by HA-PEX1 expression. An immunoblot of 8-d-old light-grown seedling extracts was serially probed with antibodies to the indicated proteins. For thiolase and PMDH, precursor (p) and mature (m) proteins are indicated. (C) PEX1 and PEX6 levels resemble WT levels in pex1-1. An immunoblot of 8-d-old light-grown seedling extracts was serially probed with antibodies to the indicated proteins. For B and C, the positions of molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated on the right and HSC70 is a loading control. (D) pex1-1 does not improve growth of pxa1-1 seedlings in the absence of sucrose. Seedlings were grown as in the legend to Fig. 1C. Bars indicate mean hypocotyl lengths (n ≥ 13), and error bars indicate SD. In A and D, means not sharing a letter above the bar are significantly different as determined by one-way ANOVA (P < 0.001).