Fig. 3.
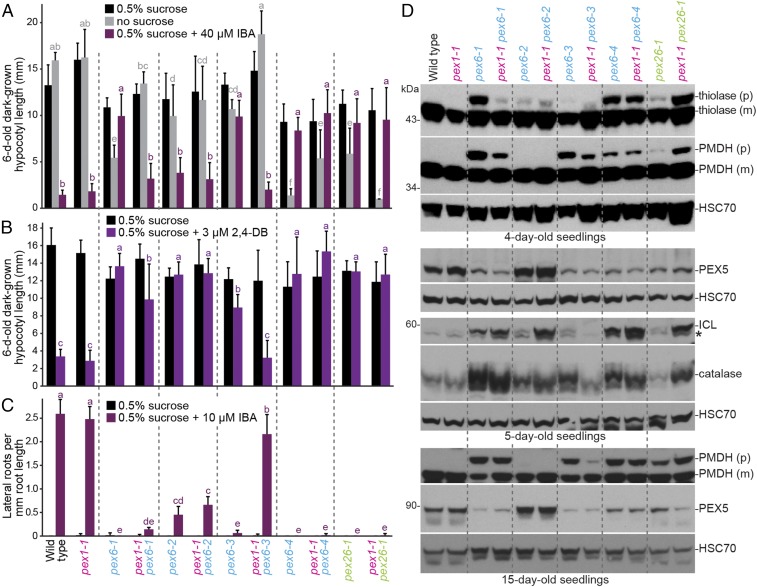
pex1-1 ameliorates pex6-1 and pex6-3 and worsens pex26-1 defects without restoring PEX5 levels. (A) pex1-1 increases the sensitivity of dark-grown pex6-1 and pex6-3 seedlings to the inhibitory effects of IBA and reduces dependence on exogenous sucrose for hypocotyl elongation but increases pex26-1 sucrose dependence. Seedlings were grown as in the legend to Fig. 1C. Bars indicate mean hypocotyl lengths (n ≥ 13), and error bars indicate SD. (B) pex1-1 increases sensitivity of dark-grown pex6-1 and pex6-3 seedlings to the inhibitory effects of 2,4-DB on hypocotyl elongation. Seedlings were grown as in the legend to Fig. 1C. Bars indicate mean hypocotyl lengths (n ≥ 12), and error bars indicate SD. (C) pex1-1 increases sensitivity of light-grown pex6-3 seedlings to the stimulatory effects of IBA on lateral root production. Seedlings were grown on control medium for 4 d followed by 4 d on medium with or without 10 μM IBA under constant yellow-filtered light. Bars indicate mean lateral root densities (n ≥ 8), and error bars indicate SD. In A–C, means not sharing a letter above the bar are significantly different as determined by one-way ANOVA (P < 0.001). (D) pex1-1 differentially impacts PTS2 processing and peroxisomal protein levels in pex6 and pex26-1 seedlings. Immunoblots of 4- (Top), 5- (Middle), and 15-d-old (Bottom) light-grown seedling extracts were serially probed with antibodies to the indicated proteins. The positions of molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated on the left. For thiolase and PMDH, precursor (p) and mature (m) proteins are indicated. HSC70 is a loading control. An asterisk indicates a cross-reacting band in the ICL panels.