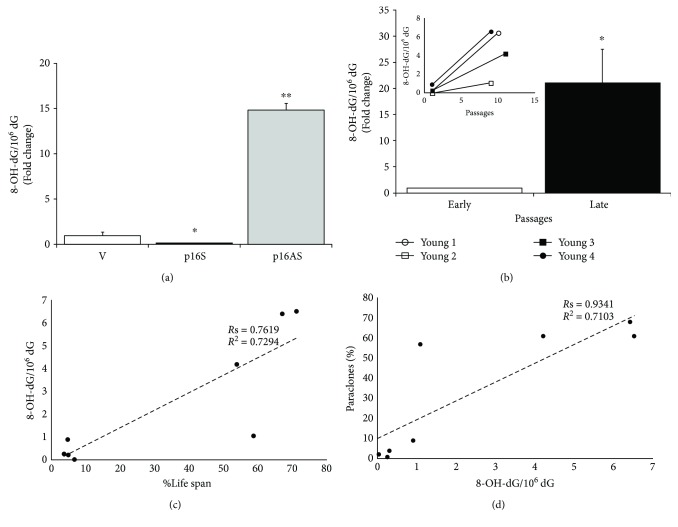
Figure 2.
Oxidative damage in senescent primary human keratinocytes. (a) DNA was isolated from empty vector-, p16 sense-, and p16-antisense-transduced primary human keratinocyte (at 2nd passage) [42], and the 8-OH-dG residue amount was determined by HPLC-ED. 2′-Deoxyguanosine (dG) was measured in the same run of corresponding 8-OH-dG, and the results were expressed as the number of 8-OH-dG residues/106dG residues. Data were shown as fold change (n = 3, ∗ p < 0.05, ∗∗ p < 0.01 by Student's test). (b) DNA was isolated from early and late passages of primary human keratinocyte cultures, and the 8-OH-dG residue amount was determined by HPLC-ED.2′-Deoxyguanosine (dG) was measured in the same run of corresponding 8-OH-dG, and the results were expressed as the number of 8-OH-dG residues/106dG residues. Data were shown as fold change (n = 4, ∗ p < 0.05 by Student's test). In the inset, the 8-OH-dG amount was reported for each strain. (c, d) The best-fit line determined by linear regression was shown for each data series, with R 2 coefficient and Spearman correlation coefficient (Rs). Two-tailed p value was reported in Result. (c) The number of cell doublings is expressed as %Life span (ratio of the number of cell doublings at selected passage on the total number of cell doublings) to take account of the life span variability among the 4 strains.