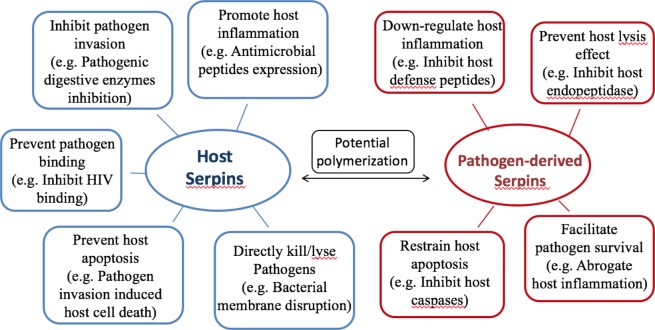
Figure 3. Summary of serpin functions in host-pathogen interactions.
Hypothesis of protective mechanisms offered byhost serpins (on the left, blue), and pathogenic mechanisms exerted by pathogen-derived serpins (on the right, red). Host serpins may act directly or indirectly upon pathogen infections. The representative mechanisms include inhibiting pathogenic digestive proteases, promoting host antimicrobial peptide expression and so on. Pathogen-derived serpins also utilize various mechanisms and representative ones are listed.