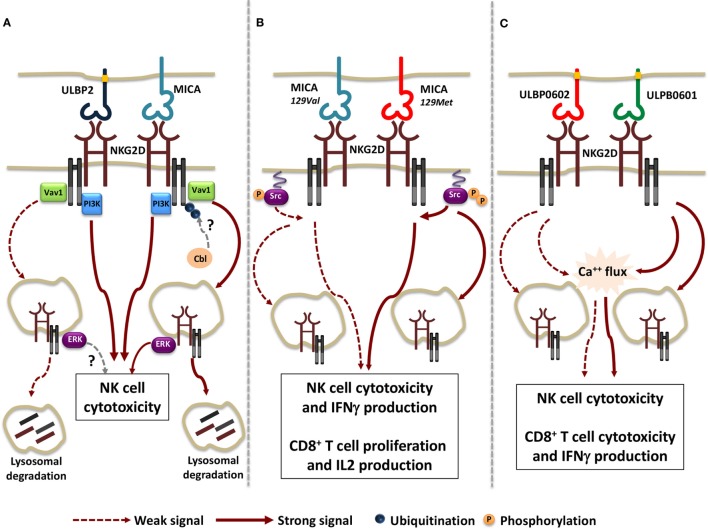
Figure 1.
Functional consequences of the interaction of NKG2D with different ligand/allelic variants. (A) Transmembrane MICA and GPI-linked ULBP2 ligands result equally able to trigger Vav1 and PI3K activation and to induce NK cell cytotoxic function. However, a stronger receptor internalization and lysosomal degradation due to the activation of the ubiquitin pathway was observed upon MICA engagement. Whether Cbl is the ubiquitin ligase regulating NKG2D/DNAX-activating protein 10 ubiquitination and whether ULBP2 ligand is able to activate NKG2D-mediated signals from endosomal compartment is not clear (dashed arrows). (B) MICA-129Met, which binds to NKG2D with higher avidity compared with MICA-129Val allele, induces stronger Src phosphorylation, thus triggering both NK cell and CD8+ T cell effector functions with higher efficiency. Concomitantly, a higher extent of NKG2D down-modulation is also induced upon MICA-129Met allele engagement. (C) The rigid and stable binding to NKG2D of the high-affinity ULBP0602 variant impairs its ability to induce Ca++ flux and effector functions in NK cell and CD8+ T cells as well as NKG2D down-modulation. As consequence, ULBP0602 engagement results less efficient compared with the low affinity variant ULBP0601.