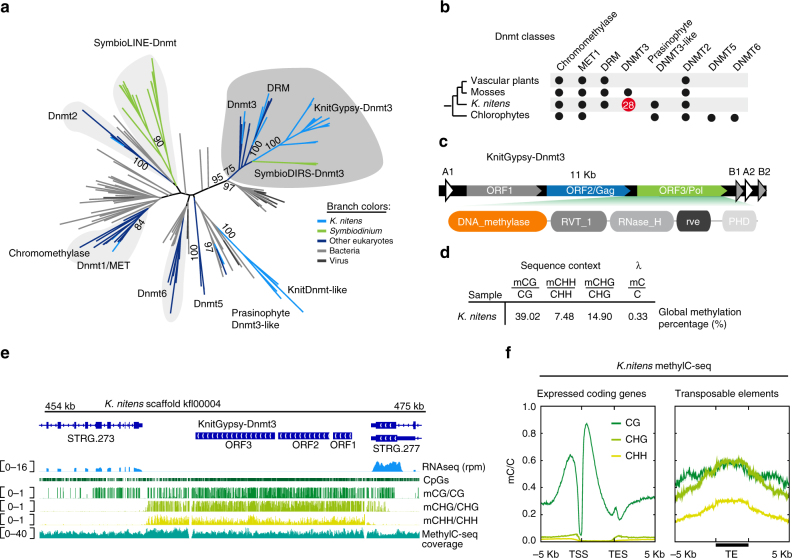
Fig. 4.
Independent Dnmt3 acquistion into K. nitens retrotransposons. a Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of eukaryotic DNMTs including K. nitens orthologs. b Distribution of DNMT classes in the viridiplantae, in red copy number of Dnmt3 found in K. nitens. c Structure of K. nitens retrotransposons that encode for DNMTs and domain architectures of the ORFs. The structure of repeats is the same as that of a DIRS retrotransposon, but the domain composition is typical of Gypsy retrotransposons. d Percentage of methylated cytosines in distinct sequence contexts in K. nitens MethylC-seq library. e Genome browser display showing the profile of cytosine methylation in CG, CHH and CHG contexts on KnitGypsy-Dnmt3 retrotransposons. rpm reads per million. f Methylation profiles in CG, CHH and CHG contexts on K. nitens genes and transposable elements. Line represents mean and pale shade represents standard error of the mean. TSS transcriptional start site, TES transcriptional end site, TE transposable element