Figure 5.
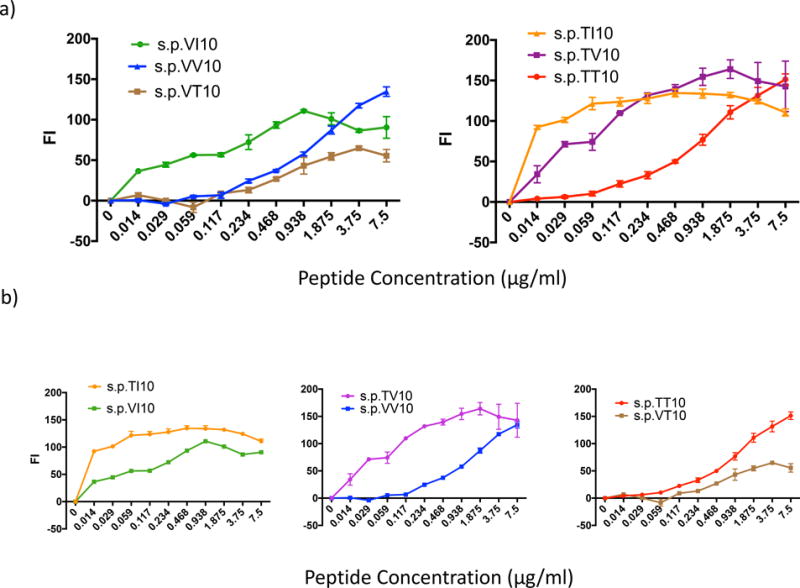
A more hydrophobic amino acid at the 323 anchor residue enhances peptide binding to the H2-Dd MHC-I molecule, while altering the 9th amino acid residue or penultimate position from the hydrophilic Thr (T322) to a more hydrophobic Val (V322) can inhibit peptide MHC I binding. Peptide induced surface expression of H-2Dd with peptides PTT10 (IGPGRAFYTT), PTI10 (IGPGRAFYTI), PTV10 (IGPGRAFYTV), PVI10 (IGPGRAFYVI), PVV10 (IGPGRAFYVV), PVT10 (IGPGRAFYVT). TAP-deficient, RMAS-Dd were incubated with indicated concentrations of each peptide and stained with the antibody 34-5-8 (an anti-H2-Dd antibody) as described in Materials and methods. Results are shown as the fluorescence index (FI), the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) over background (∆ mean fluorescence intensity) × 100 as in Fig 4b. a) Peptide affinity for the H2-Dd MHC-I molecule with the penultimate position is held constant as Val322 or Thr322 and the anchor residue is altered to either Ile323, Val323 or Thr323. Statistics: left panel, s.p.VV10 vs VT10 p = 0.0023; s.p. VV10 vs VI10 and s.p.VT10 vs VI10, p < 0.0001 by stratified Wilcoxon rank sum with Hochberg correction for multiple comparisons; right panel, s.p.TT10 differs from TV10 and TI10 at p<0.0001, but s.p.TV10 and TI10 do no differ from each other greatly. b) Peptide:MHCI binding affinity with the anchor residue (10th amino acid) held constant at Ile323, Val323 or Thr323 while the penultimate position (9th amino acid) is either Thr322 or Val322. Statistics: left panel, p < 0.0001; middle panel, p<0.0001; right panel, p<0.0001, all by the stratified Wilcoxon test.
