Fig. 3. MRCS-CD killing cancer cells in vivo.
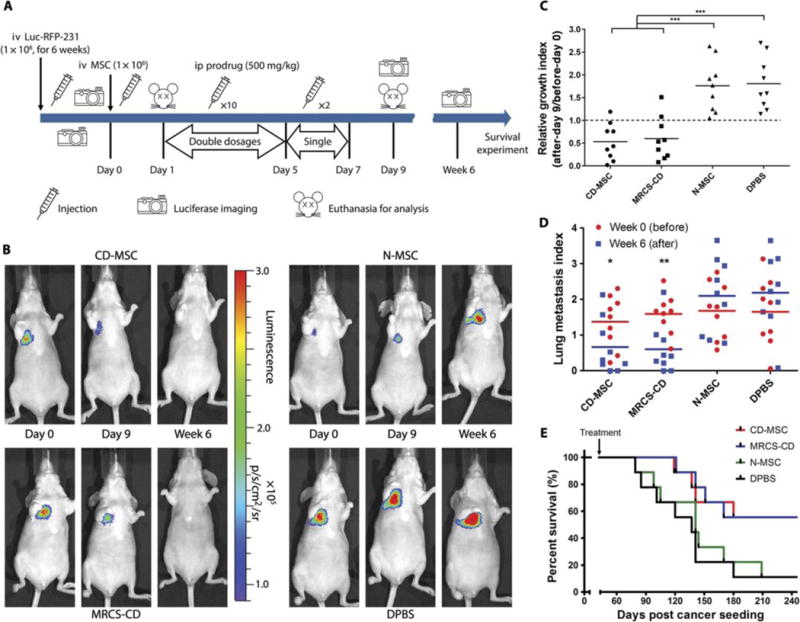
(A) Design and timeline of animal experiment to test MRCS-CD with 5-FC in vivo. iv, intravenous; ip, intraperitoneal. (B) Representative images of nude mice that received MRCS-CD treatments show that MRCS-CD decreased lung metastasis signals in vivo. Luciferase imaging was taken before (day 0, left) and after short-term 5-FC treatment (day 9, middle), as well as long-term 5-FC treatment (6 weeks, right). Quantification of luciferase signals in the lungs in vivo after (C) short-term and (D) long-termtreatments. (E) Mouse survival after MRCS-CD treatment. In (C), relative growth index = luciferase read on day 9 (after)/luciferase read on day 0 (before). In (D), lung metastasis index = log10 [(luciferase read of the tested mouse)/(luciferase read of average for tumor-free mice)]; the lung metastasis index of tumor-free mice = 0. The differences between “week 0” groups are not statistically significant. n = 9 for each group. *P <0.05, **P <0.01, and ***P <0.001. In (E), P = 0.0382, CD-MSC versus DPBS; P = 0.0429, MRCS-CD versus N-MSC; and P = 0.0211, MRCS-CD versus DPBS. Median survival (days): CD-MSC, 260; MRCS-CD, 260; N-MSC, 141; DPBS, 137.
