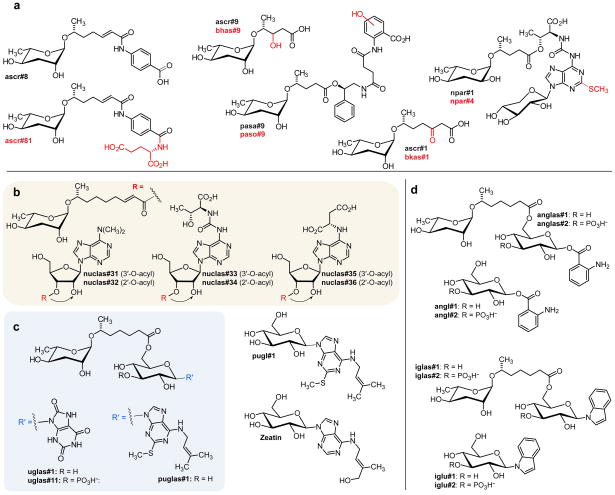
Figure 2.
a) Examples of new ascaroside derivatives closely related to previously described compounds from C. elegans (ascr#9, ascr#8, ascr#1) and P. pacificus (npar#1, pasa#9). Known structures are in black, predicted new modifications are shown in red. The structure of ascr#81 was confirmed by total synthesis. b) Structures of ascarosylated ribonucleosides. Nuclas#31–36 occur as interconverting mixtures of the 2-O- and 3-O-ascarosylated isomers. c) Ascarosylated gluconucleosides uglas#1 and puglas#1, the highly abundant pugl#1, and the plant cytokinin zeatin. c) Anthranilic acid and indole derivative anglas#1 and iglas#1. Also shown are the previously described angl#1 and iglu#1,49 which are not daf-22-dependent.