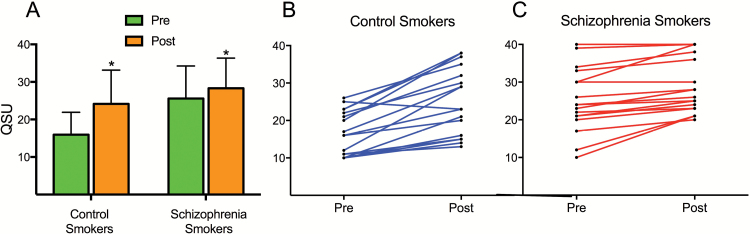
Fig. 1.
(A) Smokers with schizophrenia had higher baseline craving compared with control smokers (P ≤ .001). Both groups had greater craving after (Post) the task compared to before (Pre) the task (P ≤ .001). Control smokers had greater cue-induced increases in craving compared with smokers with schizophrenia (P = .007). QSU = Questionnaire of Smoking Urges. (B–C) Comparison of individual participant craving levels Pre and Post cue reactivity task for controls (B) and smokers with schizophrenia (C). Blunted increases in craving compared to control smokers may in part be due to ceiling effect due to maximal baseline craving in some participants. However, blunted increases in craving were seen at all levels of baseline craving.