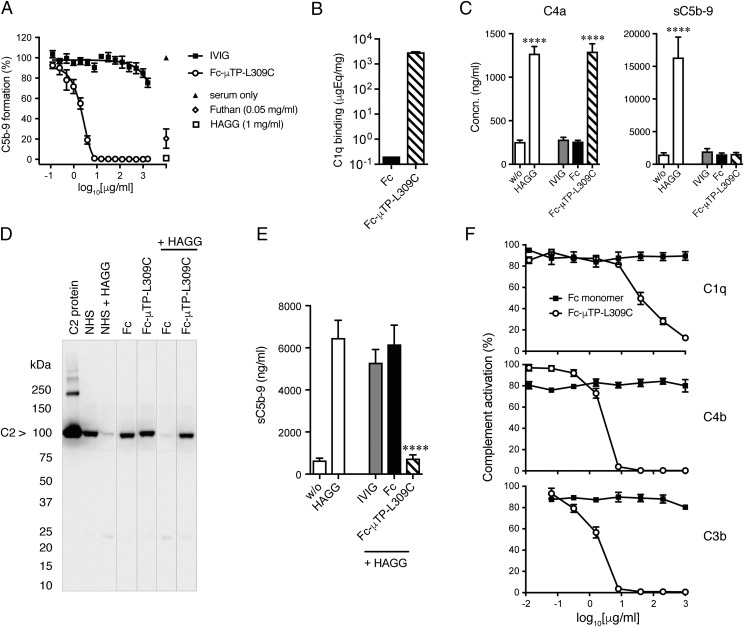
FIGURE 7.
Effects of Fc-μTP-L309C on human complement in vitro. (A) Inhibition of classical complement pathway by Fc-μTP-L309C. Wieslab ELISA Complement system kit was used. Data show the percentage of C5b-9 formation normalized to NHS values (mean ± SEM, n = 3). HAGG and Futhan served as controls. (B) Fc and Fc-μTP-L309C binding to C1q, determined by ELISA (mean ± SD, n = 2). (C) Effect of Fc-μTP-L309C on the generation of C4a (left) and sC5b-9 (right) in human whole blood. HAGG served as a positive control (mean ± SEM, n = 4). ****p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett test, compared with nonactivated. (D) Effect of Fc-μTP-L309C on C2 cleavage in the presence and absence of HAGG, demonstrated by SDS-PAGE and Western blot for C2. The position of C2 is indicated by the arrow; molecular weight markers are shown at left in kiloDaltons. Representative Western blot from three independent experiments. (E) Inhibition by Fc-μTP-L309C (1 mg/ml) of sC5b-9 generated in response to HAGG (1 mg/ml) in human whole blood (mean ± SEM, n = 4). ****p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett test, compared with HAGG. (F) Dose-dependent inhibition of C1q, C4b, and C3b deposition on HUVECs by Fc-μTP-L309C, but not Fc monomer (mean ± SEM, n = 4).