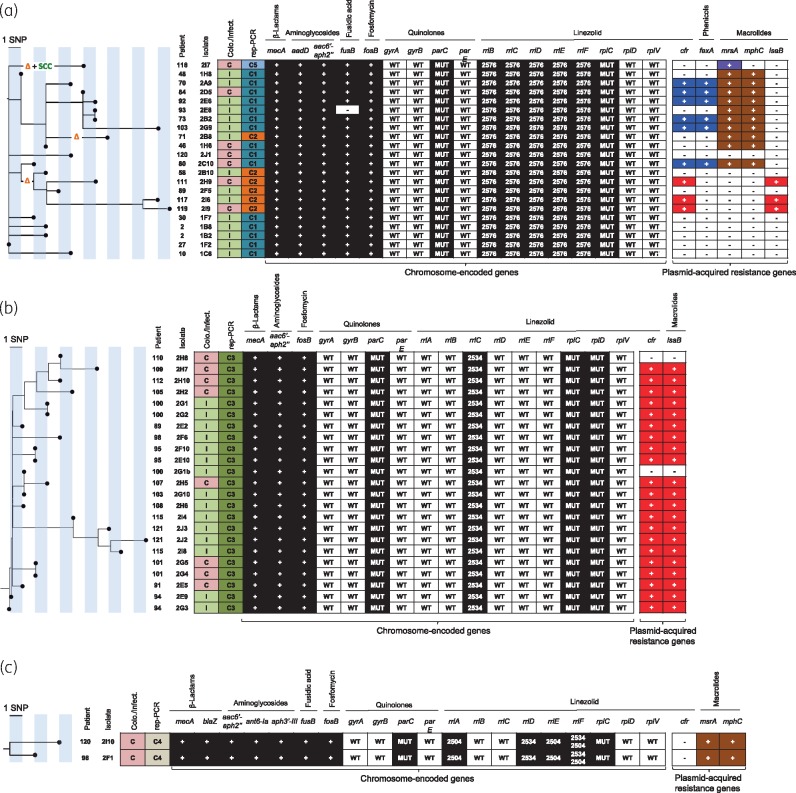
Figure 3.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on sequence variation in the core genome. (a) ST2 LRSE isolates. (b) ST5 LRSE isolates. (c) ST22 LRSE isolates. The orange Δ indicates a deletion of 13946 bp in genes located in the SCCmec cassette region (Figure S2). The green ‘SCC’ indicates the presence of an additional SCC cassette. Patient and isolate numbers are indicated on the left of the tree. Colonization or infection is indicated in the first column (C in red box for colonization, I in green box for infection). Acquired resistance genes for β-lactams, aminoglycosides, fusidic acid, fosfomycin, linezolid, phenicols and macrolides are indicated as follows: + in a dark or coloured box, presence; - in a white box, absence. Mutations in chromosome-encoded genes involved in quinolone and linezolid resistance are represented. WT, WT gene; MUT, presence of a mutation known to be responsible for phenotypic resistance; 2576, G2576U point mutation in the V domain of the 23S rRNA gene (rrl); 2534, C2534U point mutation in the V domain of the 23S rRNA gene; 2504, U2504A point mutation in the V domain of the 23S rRNA gene. Plasmid-acquired genes boxed with the same colour (purple, blue, brown and red) are located on the same plasmid [blue, p-cfr-PBR-A plasmid of 38745 bp (Figure 4a); red, p-cfr-PBR-B plasmid of 40182 bp (Figure 4b)].