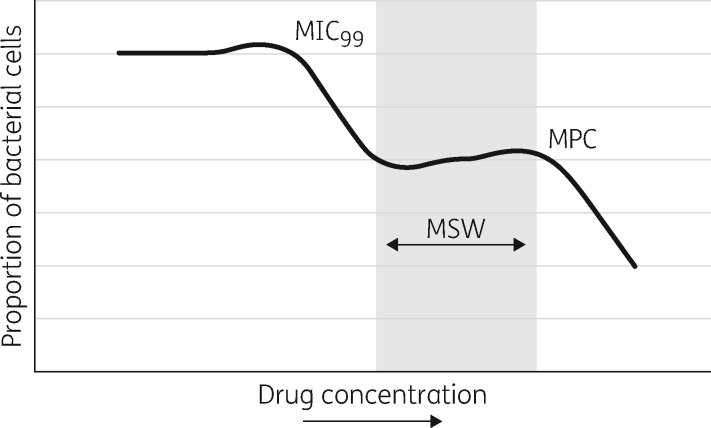
Figure 1.
Mutant selection window (MSW) hypothesis. As the concentration of the antibiotic increases, there is an initial drop in bacteria related to the inhibition of growth of 99% of susceptible cells (MIC99). This, however, then leads to a plateau as bacteria with resistance-conferring mutations are selected to grow. The second drop corresponds to the inhibition of resistant growth, termed the mutant prevention concentration (MPC). Adapted from Figure 1 in Drlica and Zhao, 2007.1