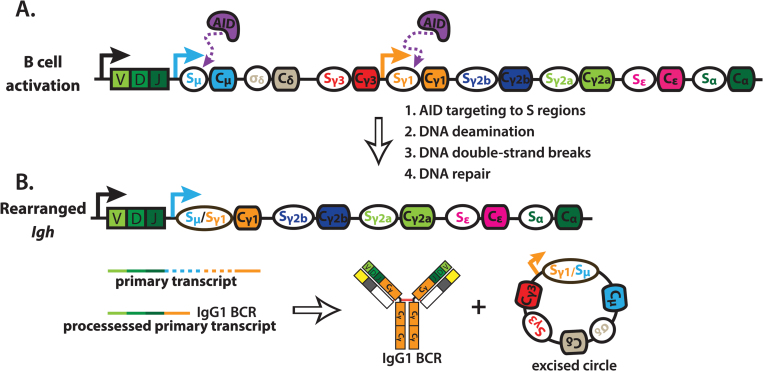
Fig. 2.
Class switch recombination. (A) B cell activation can induce expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) and transcription of downstream CH regions (orange arrow) driven by cytokine-responsive elements. This recruits AID to the downstream S region, as well as Sμ, which is constitutively transcribed. AID-mediated DNA deamination within S regions initiates the formation of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), and DNA repair occurs primarily, but not exclusively, through non-homologous end joining. (B) Repair of DNA DSBs results in a deletional-recombination event that juxtaposes the upstream V(D)J segment with a new downstream CH (indicated by Cγ1). Additionally, the excised region can ligate to form a closed circle. The class switched B cell now expresses a new B cell antigen-receptor (BCR), represented as IgG1. Solid arrows indicate transcription start sites, dashed lines within transcripts indicate introns, solid lines within transcripts indicate exons, red lines indicate disulfide bonds. AID, activation-induced cytidine deaminase.