Figure 13.
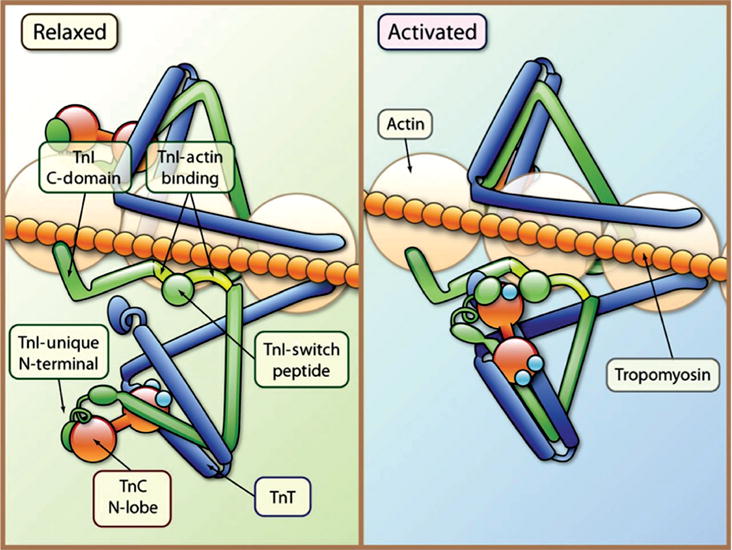
Tropomyosin and the troponin complex regulate striated muscle contraction. Each tropomyosin (orange chain) molecule is associated with one troponin complex [TnI (inhibitory-blocks myosin binding to actin; green), TnC (binds calcium; red barbells), and TnT (binds tropomyosin; blue)] and seven actin monomers. In the relaxed state tropomyosin blocks the myosin-binding site on actin. TnC is weakly bound to TnI; TnI binds to actin (TnI-actin binding) and inhibits myosin from binding to actin. Following the release of calcium (Ca2+), calcium binds to TnC and a patch of residues in the N-terminal domain of TnC is exposed and the interaction of TnC with TnI is enhanced. TnI then dissociates its inhibitory region from actin, and forms a complex with TnT and tropomyosin. Following the conformational change in the troponin complex, tropomyosin shifts and the myosin head binds to actin. [Fig. reprinted, with permission, from (642).]
