Figure 3.
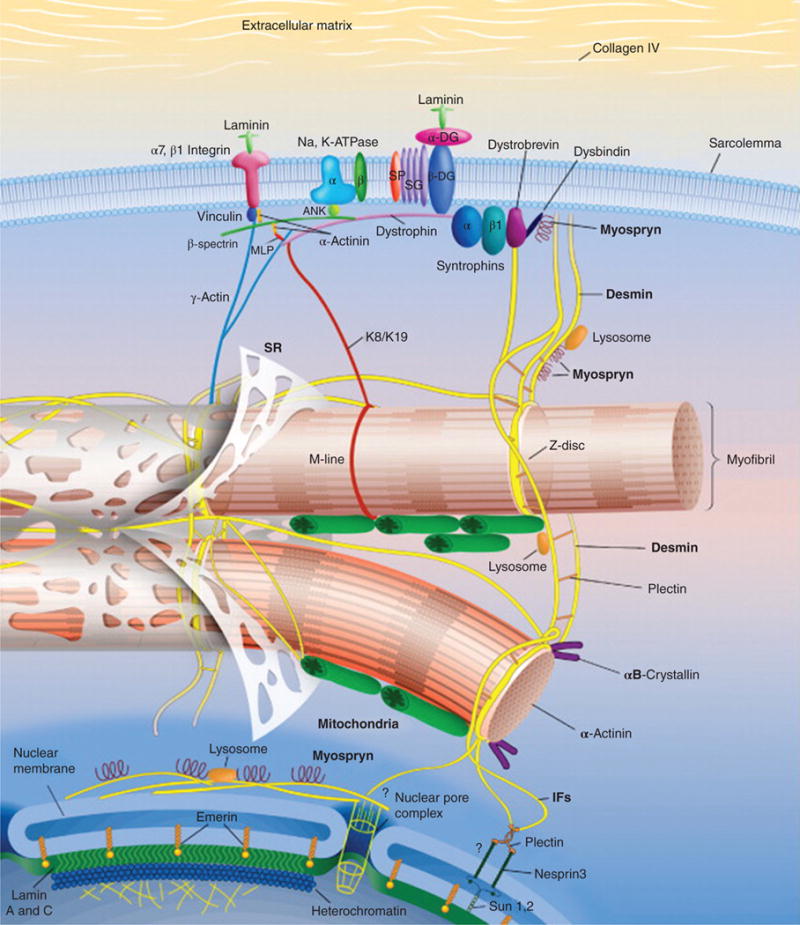
Schematic representation of the intermediate filament (IF) scaffold in striated muscle. The IF scaffold, predominantly composed of desmin (yellow), links the entire contractile apparatus to the sarcolemma and other organelles, such as the nucleus, mitochondria, lysosomes, and potentially the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR). Desmin interacts with many other proteins including synemin, paranemin, syncoilin, and myospryn. Keratins (K8/K19) link the contractile apparatus to the sarcolemma and interact with the dystrophin-dystroglycan (DG) complex. Overall, the IF scaffold helps maintain the integrity of muscle cytoarchitecture and provide mechanical strength to the cell. Abbreviations: MLP, striated muscle-specific LIM protein; SG, sarcoglycan. [Fig. modified, with permission, from (88).]
