Figure 9.
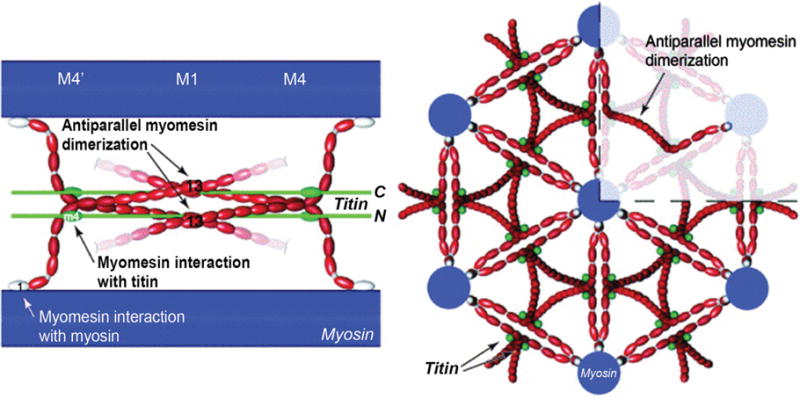
(Right) Longitudinal view of myosin (blue), myomesin (red) and titin (green). The M-band is composed of a series of electron-dense M-lines: M4, M1, and M4′ (see Fig. 1C for an electron micrograph of M-lines). Myomesin family members form antiparallel homodimers through interactions called M-bridges between the C-terminal immunoglobulin domain (labeled 13), and bind to myosin at the N-terminal domain. (Left) Cross-sectional view highlighting myomesin forming an antiparallel dimer. Myomesin acts as a thick filament cross-linking protein. [Fig. reprinted, with permission, from (9).]
