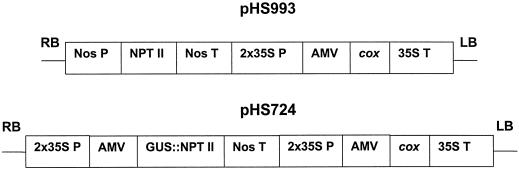
Figure 1.
T-DNA segment bound by the left (LB) and right borders (RB) of the binary vectors used in A. tumefaciens GV3101 (pMP90) (Koncz and Schell, 1986). The vectors originate in their predecessor RD400 (Datla et al., 1992). pHS993 offers selection for kanamycin resistance, whereas pHS724, which is derived from pHS723 (Hirji et al., 1996), offers this selection and also a facile screening for progeny analysis by GUS assay because of a functional fusion of GUS to neomycin phosphotransferase (nptII). The COX open reading frame from A. pascens (Rozwadowski et al., 1991) was inserted into these vectors for its expression under the control of a highly active cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter (2× 35S) expression module (Datla et al., 1993) containing the translational leader from RNA4 of alfalfa mosaic virus (AMV). Nos P, Nopaline synthase gene promoter; Nos T, nopaline synthase gene terminator; 35S T, transcription termination/polyadenylation signal of cauliflower mosaic virus from Guerineau et al. (1988).