Figure 3.
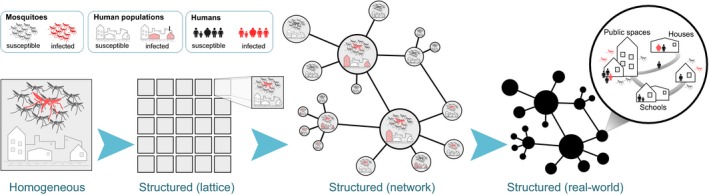
Increasing model complexity demands higher computational power. Model detail can be added by dividing a well‐mixed population into separate subpopulations, arranged in a regular spatial grid or by means of complex networks to represent geographical distribution of villages, towns and cities, with edges corresponding to major human movement patterns. Depending on data availability, more spatial and demographic detail can be added by considering individual households, places of work or schools. However, the computational demands increase significantly with more detailed information to keep track of, making the model very setting‐specific and impractical for sensitivity analyses and model fitting exercises
