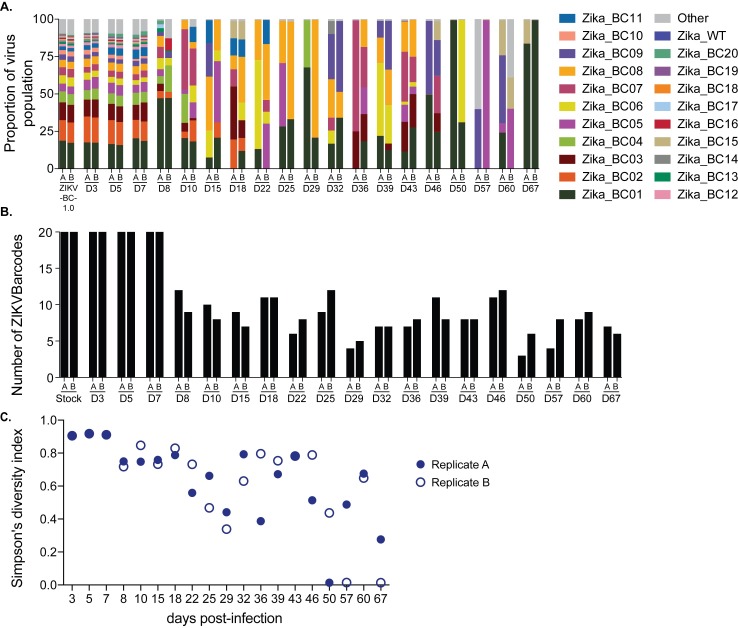
Fig 6. Sequencing of the molecular barcode isolated from pregnant animal 776301.
Viral RNA was isolated from animal 776301 at the indicated time points. The theoretical number of cDNA molecules used in each PCR reaction is shown in Table 3. For each sample, a single preparation of cDNA was made and then split into two separate PCR reactions with primer set A (178 bp) and B (131bp). PCR products were tagged and sequenced. A.) The frequency of each barcode in the population is shown for ZIKV-BC-1.0 inoculum and the animal 776301. The frequency of the wild type sequence in the region of the barcode is shown as Zika_WT. The frequency of any sequence in the region of the barcode that was not considered authentic is listed as ‘Other.’ B.) The number of authentic barcodes detected in animal 776301 were counted for each sample and the data for each individual replicate are shown. C.) Average genetic complexity at the barcode positions measured by Simpson’s diversity index. Closed symbols represent Simpson’s diversity index in replicate A samples and open symbols represent Simpson’s diversity index in replicate B.